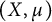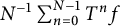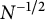Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1416831 results in Open Access
Sanitary-Hygienic Research to Ensure State Sanitary-Epidemiological Surveillance in the Republic of Kazakhstan
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, e249
-
- Article
- Export citation
Interaction between green tea and metformin and its effects on oxidative stress and inflammation in overweight women: a randomised clinical trial
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 132 / Issue 9 / 14 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 1173-1181
- Print publication:
- 14 November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Continuity and change: A review of The United States of English - Rosemarie Ostler, The United States of English – The American Language from Colonial Times to the Twenty-First Century Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2023. Pp. 233+appendices. Hardback £21.99, ISBN 9780197647295
-
- Journal:
- English Today / Volume 40 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 306-307
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Recommendations on Imaging in the Context of Alzheimer’s Disease-Modifying Therapies from the CCNA Imaging Workgroup
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 52 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 623-631
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
BWC confidence-building measures: Increasing BWC assurance through transparency and information sharing
-
- Journal:
- Politics and the Life Sciences / Volume 44 / Issue 1 / Spring 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 5-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nuclear existentialism: On the philosophical response to life and death under the bomb
-
- Journal:
- Review of International Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Laura Mamo, Sexualizing Cancer: HPV and the Politics of Cancer Prevention Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2024. Pp. 360. ISBN 978-0-226-82929-6. $35.00 (paper).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 357-358
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Promoting employees’ innovative work behavior through innovation-specific leader behavior: An AMO-approach
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization / Volume 31 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 215-232
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Forgotten Sex: Modern Responses to Correlative Sexism in Kang Youwei and He-Yin Zhen
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Diagnosis, prevention and management of delirium: spot it, stop it, treat it
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Advances , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Value-driven Contention in China: Forms, Tactics and State Responses
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 261 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 39-56
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
When education is positional: higher education expansion, welfare regimes and income inequality
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Social Policy , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations of saccharin intake with all-cause, cardiovascular and cancer mortality risk in USA adults
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 132 / Issue 9 / 14 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 1205-1213
- Print publication:
- 14 November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Scales and self-sustained mechanism of reattachment unsteadiness in separated shock wave/boundary layer interaction
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 998 / 10 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, A54
-
- Article
- Export citation
Associations of various healthy dietary patterns with biological age acceleration and the mediating role of gut microbiota: results from the China Multi-Ethnic Cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 132 / Issue 11 / 14 December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 1490-1502
- Print publication:
- 14 December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inventors among the “Impoverished Sophisticate”
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Economic History / Volume 84 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 1175-1207
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fossil Fuel Industry Divestment and the Energy Transition: Lessons and Red Flags from Shell and the Niger Delta
-
- Journal:
- Business and Human Rights Journal / Volume 9 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 301-307
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Is an antioxidant-rich or a pro-inflammatory diet during pregnancy associated with allergic and respiratory multimorbidity in children from the ELFE birth cohort?
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 132 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 1356-1364
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the speed of convergence in the ergodic theorem for shift operators
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multifunctional and tunable bandpass filters with RF codesigned isolator and impedance matching capabilities
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 17 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2024, pp. 303-317
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation