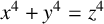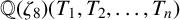Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1417116 results in Open Access
Maternal labor supply and children's emotional well-being
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Demographic Economics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1-47
-
- Article
- Export citation
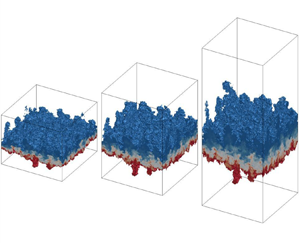
Impact of axial strain on linear, transitional and self-similar turbulent mixing layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 999 / 25 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, A5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sex Differences in Moderate-to-Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Randomized Controlled Trials
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 52 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 411-420
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Trends in Twin Births and Survival in Rural Spain: Evidence from 18th to 20th Century
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 27 / Issue 6 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 302-310
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
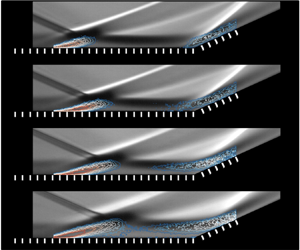
On the mean structure and unsteadiness of dual shock wave–turbulent boundary layer interactions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 999 / 25 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, A3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Jonathan R. Cole, Smoother Pebbles: Essays in the Sociology of Science New York: Columbia University Press, 2024. Pp. 680. ISBN 978-0-231-21261-8. £35.00 (paperback).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 387-388
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Kate MacCord, How Does Germline Regenerate? Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2024. Pp. 168. ISBN 978-0-226-83051-3. $26.00 (paper).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 373-374
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Co-creation and recovery in mental health services: a lived experience perspective
-
- Journal:
- Irish Journal of Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Response to “A Case Study of Academic Facilitation of the Global Illicit Trade in Cultural Objects: Mary Slusser in Nepal,” International Journal of Cultural Property (2023), 1–20, Emiline Smith and Erin Thompson
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Cultural Property / Volume 30 / Issue 4 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 446-447
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Geneticization of Education and Its Bioethical Implications
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Quarterly of Healthcare Ethics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Acute myocarditis in a paediatric patient with pre-existing dilated cardiomyopathy following SARS-COV-2 infection: a journey from decompensation to heart transplantation
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 10 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 2244-2247
-
- Article
- Export citation
Beyond the Budget: A Global Perspective on Social Spending through Tax Expenditures
-
- Journal:
- Social Policy and Society / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 333-351
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Medicalization of Sufism: the discourse of psychiatry, psychopathology, and secularity in Karay’s Kadınlar Tekkesi
-
- Journal:
- New Perspectives on Turkey , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
US conservative advocacy organizations and right-wing legal mobilization in Europe
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Law in Context / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 307-323
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mapping the potentials and pitfalls of using European law for strategic litigation against illiberal reforms
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Law in Context / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 379-400
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
POINTS ON
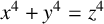 $x^4+y^4=z^4$ OVER QUADRATIC EXTENSIONS OF
$x^4+y^4=z^4$ OVER QUADRATIC EXTENSIONS OF 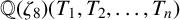 ${\mathbb {Q}}(\zeta _8)(T_1,T_2,\ldots ,T_n)$
${\mathbb {Q}}(\zeta _8)(T_1,T_2,\ldots ,T_n)$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 111 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 19-31
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
School connectedness as a protective factor between childhood adversity and adolescent mental health outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 37 / Issue 3 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1355-1373
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Feminism's Fight: Challenging Politics and Policies in Canada Since 1970 Barbara Cameron and Meg Luxton, eds. Vancouver: UBC Press, 2023, pp. 392. 10.59962/9780774868051
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique / Volume 57 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 717-719
-
- Article
- Export citation
Shalyn Claggett. Equal Natures: Popular Brain Science and Victorian Women's Writing Studies in the Long Nineteenth Century. Albany: SUNY Press, 2023. Pp. 272. $99.00 (paper).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 63 / Issue 4 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 939-941
-
- Article
- Export citation