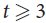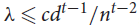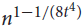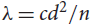Refine search
Actions for selected content:
48532 results in Computer Science
Frontmatter
-
- Book:
- Competitive Programming in Python
- Published online:
- 03 December 2020
- Print publication:
- 17 December 2020, pp i-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The potential use of pumice in mine backfill
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 December 2020, e56
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

Natural Language Processing
- A Machine Learning Perspective
-
- Published online:
- 16 December 2020
- Print publication:
- 07 January 2021
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
NLE volume 27 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Natural Language Engineering / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2020, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
NLE volume 27 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Natural Language Engineering / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2020, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A basic human values approach to migration policy communication
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 2 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2020, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GPT-3: What’s it good for?
-
- Journal:
- Natural Language Engineering / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2020, pp. 113-118
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Processing negation: An introduction to the special issue
-
- Journal:
- Natural Language Engineering / Volume 27 / Issue 2 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2020, pp. 119-120
-
- Article
- Export citation
Manipulation of Articulated Objects Using Dual-arm Robots via Answer Set Programming
-
- Journal:
- Theory and Practice of Logic Programming / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2020, pp. 372-401
-
- Article
- Export citation
RATIO ESTIMATION OF THE POPULATION MEAN USING AUXILIARY INFORMATION UNDER THE OPTIMAL SAMPLING DESIGN
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 36 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2020, pp. 449-460
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Probabilistic Description Logic
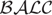
-
- Journal:
- Theory and Practice of Logic Programming / Volume 21 / Issue 4 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2020, pp. 404-427
-
- Article
- Export citation
Near-perfect clique-factors in sparse pseudorandom graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 30 / Issue 4 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2020, pp. 570-590
-
- Article
- Export citation
Policy priority inference: A computational framework to analyze the allocation of resources for the sustainable development goals
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 2 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2020, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
DRAT: Data risk assessment tool for university–industry collaborations
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2020, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A CUMULATIVE RESIDUAL INACCURACY MEASURE FOR COHERENT SYSTEMS AT COMPONENT LEVEL AND UNDER NONHOMOGENEOUS POISSON PROCESSES
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 36 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2020, pp. 294-319
-
- Article
- Export citation

The Dialogical Roots of Deduction
- Historical, Cognitive, and Philosophical Perspectives on Reasoning
-
- Published online:
- 10 December 2020
- Print publication:
- 17 December 2020

Essentials of Pattern Recognition
- An Accessible Approach
-
- Published online:
- 08 December 2020
- Print publication:
- 19 November 2020
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
Quantifying the effects of passenger-level heterogeneity on transit journey times
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 December 2020, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
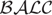
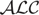 . We present a tableau-based procedure for deciding consistency and adapt it to solve other probabilistic, contextual, and general inferences in this logic. We also show that all these problems remain ExpTime-complete, the same as reasoning in the underlying classical
. We present a tableau-based procedure for deciding consistency and adapt it to solve other probabilistic, contextual, and general inferences in this logic. We also show that all these problems remain ExpTime-complete, the same as reasoning in the underlying classical