Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
205 results in 12xxx
Hypertranscendance des systèmes aux différences diagonaux
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 144 / Issue 3 / May 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 May 2008, pp. 565-581
- Print publication:
- May 2008
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Dwork’s conjecture on the logarithmic growth of solutions of p-adic differential equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 144 / Issue 2 / March 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2008, pp. 484-494
- Print publication:
- March 2008
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Facteurs epsilon p-adiques
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 144 / Issue 2 / March 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2008, pp. 439-483
- Print publication:
- March 2008
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On Construction of Saturated Distinguished Chains
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 54 / Issue 1-2 / December 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2009, pp. 59-65
- Print publication:
- December 2007
-
- Article
- Export citation
Local solutions to positive characteristic non-Archimedean differential equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 143 / Issue 6 / November 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 November 2007, pp. 1465-1477
- Print publication:
- November 2007
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Resolution in hölder spaces of an elliptic problem in an unbounded domain
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 81 / Issue 3 / December 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 387-404
- Print publication:
- December 2006
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Problèmes de ruine en théorie du risque à temps discret avec horizon fini
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / September 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 527-542
- Print publication:
- September 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Probabilité de ruine éventuelle dans un modèle de risque à temps discret
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / September 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 543-556
- Print publication:
- September 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
On minimal pairs and residually transcendental extensions of valuations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 93-106
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
On extensions generated by roots of lifting polynomials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 107-118
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Difference polynomials and their generalizations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 48 / Issue 1-2 / December 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 293-299
- Print publication:
- December 2001
-
- Article
- Export citation
Factorization over local fields and the irreducibility of generalized difference polynomials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 47 / Issue 1-2 / December 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 173-196
- Print publication:
- December 2000
-
- Article
- Export citation
The orders of nonsingular derivations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / October 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 254-260
- Print publication:
- October 1999
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A generalized fundamental principle
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 46 / Issue 1 / June 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 83-92
- Print publication:
- June 1999
-
- Article
- Export citation
Representation formulas for entire functions of exponential type and generalized bernoulli polynomials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / June 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 307-316
- Print publication:
- June 1998
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On a generalization of Eisenstein's irreducibility criterion
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 44 / Issue 1 / June 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 37-41
- Print publication:
- June 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
The locally convex topology on the space of meromorphic functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 59 / Issue 3 / December 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 287-303
- Print publication:
- December 1995
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On Schur's conjecture
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 58 / Issue 3 / June 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 312-357
- Print publication:
- June 1995
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Kronecker classes of fields and covering subgroups of finite groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 57 / Issue 1 / August 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 17-34
- Print publication:
- August 1994
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Prolongations of valuations to simple transcendental extensions with given residue field and value group
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 38 / Issue 2 / December 1991
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 386-390
- Print publication:
- December 1991
-
- Article
- Export citation
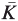 of
of 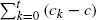 is bounded as the time
is bounded as the time 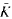 of
of 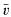 its unique prolongation to a fixed algebraic closure
its unique prolongation to a fixed algebraic closure 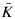 of
of 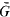 . For any subfield
. For any subfield 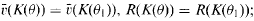 in case (
in case (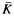 of
of 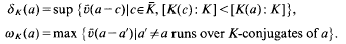
 is an inclusion of totally ordered abelian groups with [
is an inclusion of totally ordered abelian groups with [