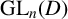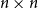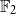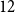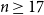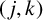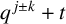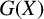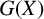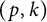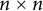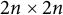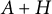Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
211 results in 15Axx
Completion problems and sparsity for Kemeny’s constant
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 1-18
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
LOCALLY NILPOTENT SUBGROUPS OF
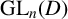 $\mathrm {GL}_n(D)$
$\mathrm {GL}_n(D)$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 112 / Issue 1 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 128-138
- Print publication:
- August 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Height functions on Hecke orbits and the generalised André–Pink–Zannier conjecture
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 160 / Issue 11 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 2531-2584
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A mathematical theory of super-resolution and two-point resolution
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 October 2024, e83
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A CONJECTURE OF ZHI-WEI SUN ON MATRICES CONCERNING MULTIPLICATIVE SUBGROUPS OF FINITE FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 111 / Issue 3 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 490-496
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A new formula for the determinant and bounds on its tensor and Waring ranks
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 769-794
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
CHARACTERISTIC POLYNOMIALS OF THE MATRICES WITH
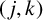 $(\,j,k)$-ENTRY
$(\,j,k)$-ENTRY 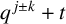 $q^{\,j\pm k}+t$
$q^{\,j\pm k}+t$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 111 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 228-237
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A reproducing kernel approach to Lebesgue decomposition
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 77 / Issue 5 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2024, pp. 1570-1610
- Print publication:
- October 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
INVERSE CONNECTION FORMULAE FOR GENERALISED BESSEL POLYNOMIALS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 110 / Issue 3 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2024, pp. 480-487
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON GENERALISED LEGENDRE MATRICES INVOLVING ROOTS OF UNITY OVER FINITE FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 110 / Issue 2 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, pp. 199-210
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
A generalization of immanants based on partition algebra characters
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, pp. 1001-1010
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
MAXIMAL SUBSEMIGROUPS OF INFINITE SYMMETRIC GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 110 / Issue 2 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 324-337
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Linear maps preserving
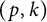 $(p,k)$-norms of tensor products of matrices
$(p,k)$-norms of tensor products of matrices
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 77 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, pp. 187-207
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Unified bounds for the independence number of graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 77 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 97-117
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
The blowup-polynomial of a metric space: connections to stable polynomials, graphs and their distance spectra
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 76 / Issue 6 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2023, pp. 2073-2114
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Norms on complex matrices induced by random vectors II: extension of weakly unitarily invariant norms
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 447-457
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
SOME COUNTING QUESTIONS FOR MATRIX PRODUCTS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 110 / Issue 1 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 32-43
- Print publication:
- August 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
ON EXTERIOR POWERS OF REFLECTION REPRESENTATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 110 / Issue 1 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 October 2023, pp. 90-102
- Print publication:
- August 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Block perturbation of symplectic matrices in Williamson’s theorem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2023, pp. 201-214
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Erdős–Ko–Rado theorem in Peisert-type graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2023, pp. 176-187
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation