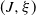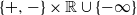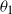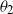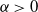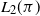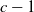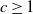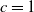Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52666 results in Statistics and Probability
Sequential metric dimension for random graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 909-951
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Necessity of weak subordination for some strongly subordinated Lévy processes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 868-879
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the finiteness and tails of perpetuities under a Lamperti–Kiu MAP
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 1086-1113
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Arcsine laws for random walks generated from random permutations with applications to genomics
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 851-867
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Percolation phase transition in weight-dependent random connection models
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 1090-1114
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
On point processes defined by angular conditions on Delaunay neighbors in the Poisson–Voronoi Tessellation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 952-965
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exact simulation of coupled Wright–Fisher diffusions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 923-950
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bounds on the mean and squared coefficient of variation of phase-type distributions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 880-889
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multitype branching process with non-homogeneous Poisson and contagious Poisson immigration
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 1007-1042
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
A stochastic matching model on hypergraphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 951-980
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Assortment of kaempferol and zinc gluconate improves noise-induced biochemical imbalance and deficits in body weight gain
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 2 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A restaurant process with cocktail bar and relations to the three-parameter Mittag–Leffler distribution
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 978-1006
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sparse regular variation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 1115-1148
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
JPR volume 58 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Approximations of geometrically ergodic reversible markov chains
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 981-1022
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
APR volume 53 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Clustering in preferential attachment random graphs with edge-step
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 890-908
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Two poisson limit theorems for the coupon collector’s problem with group drawings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 966-977
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Shot noise processes with randomly delayed cluster arrivals and dependent noises in the large-intensity regime
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 1190-1221
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
APR volume 53 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation