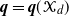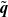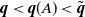Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52383 results in Statistics and Probability
Emerging health data platforms: From individual control to collective data governance
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 2 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2020, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Global Health Security index and Joint External Evaluation score for health preparedness are not correlated with countries' COVID-19 detection response time and mortality outcome
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2020, e210
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Survival and predictors of deaths of patients hospitalised due to COVID-19 from a retrospective and multicentre cohort study in Brazil
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2020, e198
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
D-dimer levels on admission and all-cause mortality risk in COVID-19 patients: a meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2020, e202
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Data-driven surrogate modeling and benchmarking for process equipment
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2020, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ALGEBRAIC RELIABILITY OF MULTI-STATE k-OUT-OF-n SYSTEMS—CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2020, p. 1005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Retrospective analysis of clinical features in 134 coronavirus disease 2019 cases
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 September 2020, e199
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Gradient and Harnack-type estimates for PageRank
-
- Journal:
- Network Science / Volume 9 / Issue S1 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 September 2020, pp. S4-S22
-
- Article
- Export citation
The spatio-temporal epidemic dynamics of COVID-19 outbreak in Africa
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2020, e212
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Does incubation period of COVID-19 vary with age? A study of epidemiologically linked cases in Singapore
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2020, e197
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Changes in psychological wellbeing, attitude and information-seeking behaviour among people at the epicentre of the COVID-19 pandemic: a panel survey of residents in Hubei province, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2020, e201
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The importance of distinguishing COVID-19 from more common respiratory illnesses
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2020, e195
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Single-seed cascades on clustered networks
-
- Journal:
- Network Science / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2020, pp. 59-72
-
- Article
- Export citation
One- versus multi-component regular variation and extremes of Markov trees
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 52 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 September 2020, pp. 855-878
- Print publication:
- September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Superbubbles as an empirical characteristic of directed networks
-
- Journal:
- Network Science / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2020, pp. 49-58
-
- Article
- Export citation
Existence of Gibbs point processes with stable infinite range interaction
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 57 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2020, pp. 775-791
- Print publication:
- September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the behavior of the failure rate and reversed failure rate in engineering systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 57 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2020, pp. 899-910
- Print publication:
- September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
The probabilities of extinction in a branching random walk on a strip
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 57 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2020, pp. 811-831
- Print publication:
- September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
APR volume 52 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 52 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 September 2020, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- September 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ASB volume 50 issue 3 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 50 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2020, pp. b1-b5
- Print publication:
- September 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation