Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418601 results in Open Access
Revisiting Brenner's method for Stokes resistance of a deformed sphere
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 994 / 10 September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, A17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Emmanuel Durand, O.P., Divine Speech in Human Words: Thomistic Engagements with Scripture, ed. Matthew K. Minerd (Washington, DC: CUA Press, 2022), pp. xv + 460. $65.00
-
- Journal:
- Scottish Journal of Theology / Volume 78 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 76-78
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Witnessing flows in arithmetic
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Structures in Computer Science / Volume 34 / Issue 7 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 578-614
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Market Failure, Information Asymmetries, and Monopoly Profits: The Barranquilla Railway and Pier Company in Colombia, 1888–1933
-
- Journal:
- Enterprise & Society / Volume 26 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 677-708
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Gender Conflicts on the Shopfloor: Barcelona Women at Chocolates Amatller, 1890–1914
-
- Journal:
- International Review of Social History / Volume 69 / Issue 2 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 230-257
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
From where I belong: using mitochondrial DNA analysis to investigate the origin of a white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) captured in Indonesian waters
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, e75
-
- Article
- Export citation
Gujarat Under Modi: Laboratory of Today's India By Christophe Jaffrelot. London: Hurst (dist. Oxford University Press), 2024. 416 pages. Hardback, £30.00 GBP, ISBN: 9781849044295
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Asian Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
- Export citation
Science of Norms as the Next Phase of the Sociology of Law and Socio-Legal Scholarship - Sociology of Law as the Science of Norms. By Hakan Hyden, New York: Routledge, 2022, 328 pp. Paperback, US$52.00
-
- Journal:
- Asian Journal of Law and Society / Volume 11 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 216-222
-
- Article
- Export citation
ON GROUPS AND FIELDS DEFINABLE IN
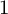 $1$-H-MINIMAL FIELDS
$1$-H-MINIMAL FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 203-248
- Print publication:
- January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The diversity, distribution, and taxonomic history of the Brazilian Tanaidacea (Crustacea)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, e71
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of substrate water content on maturation feeding of Monochamus galloprovincialis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae)
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 156 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fire in Jamaica, 1831–32
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 63 / Issue 4 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 772-791
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.A. Allum, Dear All: Letters from Europe. An Englishman in Naples, Perugia and Marseille (1956–1958) edited by M.P. Allum and Felia Allum, Naples, Editoriale Scientifica, 2024, 218 pp., €18 (paperback), ISBN 9791259768483
-
- Journal:
- Modern Italy / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 121-123
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
EXPERIMENTAL CONDITIONS FOR 14C GRAPHITE PREPARATION AT THE GXNU LAB, CHINA
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 66 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 1322-1334
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Omobranchus sewalli (Valenciennes, 1836) an established species in the South Brazil
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, e70
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mwene Muji: A Medieval Empire in Central Africa?
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of African History / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 30-46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Individual versus group morality: the role of information
-
- Journal:
- Economics & Philosophy / Volume 41 / Issue 2 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 252-275
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of degassing on bubble populations in air-entraining free-surface turbulent flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 995 / 25 September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, A12
-
- Article
- Export citation
The times, they are a-changing: Australian secondary classroom music teachers reflect on their early career 40 years on
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Music Education / Volume 42 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 110-123
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Adam Ployd, Augustine, Martyrdom, and Classical Rhetoric (Oxford: OUP, 2023), pp. xi + 165. $83.00
-
- Journal:
- Scottish Journal of Theology / Volume 77 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 412-413
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation