Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418615 results in Open Access
DT INVARIANTS FROM VERTEX ALGEBRAS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 291-339
- Print publication:
- January 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Particle chirality does not matter in the large-scale features of strong turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 995 / 25 September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, A10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Post Nubes Lux
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1325 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 1323-1324
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cold-water coral Dendrophyllia ramea as a habitat-forming species in shallow coastal waters: its role in a vulnerable ecosystem and anthropogenic impacts
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, e72
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
THE SLICE-BENNEQUIN INEQUALITY FOR THE FRACTIONAL DEHN TWIST COEFFICIENT
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 273-289
- Print publication:
- January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PARITY OF CONJUGATE SELF-DUAL REPRESENTATIONS OF INNER FORMS OF
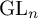 $\operatorname { {GL}}_n$ OVER p-ADIC FIELDS
$\operatorname { {GL}}_n$ OVER p-ADIC FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 249-271
- Print publication:
- January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Seven Sacraments of the Catholic Church by Romanus CessarioO.P., Baker Academic, Grand Rapids, Michigan, 2023, pp. xiv+290, $32.99, hbk
-
- Journal:
- New Blackfriars / Volume 105 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 683-686
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Meanings of disrupted everyday (im)mobilities in later life: running daily errands before and during the pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Ageing & Society / Volume 45 / Issue 7 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 1287-1305
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sea turtle stranding records and fishing interactions on an Oceanic Atlantic Island (Tenerife, Canary Islands)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, e82
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
14C MICROSAMPLE ANALYSIS WITH ECHoMICADAS FACILITIES: CURRENT STATE OF PLAY
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 66 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 1379-1394
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
PALEO TSUNAMIS AND STORM SURGES RECORDED BY FOSSIL CORAL ON YAKUSHIMA ISLAND, JAPAN
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 66 / Issue 6 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 1914-1928
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Allostatic load and cognitive recall among young adults: Racial, ethnic, and sex-specific variations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 8 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 755-763
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sleep-related measurements to assess sleep disturbances among people living with dementia in nursing homes: a systematic review
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 36 / Issue 12 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 1128-1156
-
- Article
- Export citation
Measuring clinically relevant change in apathy symptoms in ADMET and ADMET 2
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 36 / Issue 12 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 1232-1244
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chinese primers along the north-western frontier
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 711-728
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Outcomes after bidirectional cavopulmonary shunt with antegrade pulmonary blood flow in high-risk patients
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 10 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 2122-2131
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sylvain Pattieu, Emmanuelle Sibead, and Tyler Stovall. The Black Populations of France: Histories from Metropole to Colony. Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press, 2021. 236 pp. 5 charts. Index. $30. Paper. ISBN: 978-1-4962-2899-4.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 1092-1093
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Social Constitution: Embedding Social Rights through Legal Mobilization, by Whitney K. Taylor, Cambridge and New York, Cambridge University Press, 2023. Tables, figures, appendix, bibliography, index, 254 pp., hardcover $125.00.
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Politics and Society / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 160-163
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Malacca dilemma of the Raj: the Indian Uprising of 1857, the Second Opium War, and the British proposal of a Kra passage
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 821-836
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Social cognition and healthy aging: Cross-sectional associations of emotion perception, theory of mind, and emotional empathy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 9 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 801-806
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation