Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1421770 results in Open Access
CONGRUENCES FOR SUMS OF MACMAHON’S q-CATALAN POLYNOMIALS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 111 / Issue 3 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 416-427
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Biological properties of vitamin B12
-
- Journal:
- Nutrition Research Reviews / Volume 38 / Issue 1 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 338-370
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Controversies in trauma- and stress-related disorders
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 226 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 7-9
- Print publication:
- January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Stalking and autism
-
- Journal:
- Irish Journal of Psychological Medicine / Volume 41 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 510-511
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Oxygen saturation measurement in cyanotic heart disease with the Apple watch
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 9 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 1971-1973
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Energy-based characterisation of large-scale coherent structures in turbulent pipe flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 996 / 10 October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, A45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rotational Taylor dispersion in linear flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 997 / 25 October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, A10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bishops, Canon Law and Governance in Tenth-Century England: the Constitutiones of Oda of Canterbury
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Ecclesiastical History / Volume 76 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 25-54
- Print publication:
- January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dejustifying Scientific Progress
-
- Journal:
- Philosophy of Science / Volume 92 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 488-495
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ROMAN URBANISM IN ITALY: EXPLORING NEW AND TRADITIONAL APPROACHES
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 75 / Issue 1 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 53-62
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Shock persistence, uncertainty, and news-driven business cycles
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 29 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, e43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterizing English Preposing in PP constructions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Linguistics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 1-39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Complex Legacy - Andrew Garrett, The Unnaming of Kroeber Hall: Language, Memory, and Indigenous California (Cambridge Massachusetts, MIT Press, 2023, 472 p.)
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Sociology / Archives Européennes de Sociologie / Volume 65 / Issue 3 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 436-441
-
- Article
- Export citation
A. J. BOYLE (ED.), SENECA HERCULES, EDITED WITH INTRODUCTION, TRANSLATION AND COMMENTARY. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press, 2023. Pp. xiii + 789. isbn 9780198856948 (hbk). £190.00.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies / Volume 114 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 184-185
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the reduction of flow rate losses using thermal waves
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 997 / 25 October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, A12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
AFH volume 65 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of African History / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. b1-b3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Ownership and Inheritance in Sanskrit Jurisprudence. By Christopher T. Fleming. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2021. Pp. 272. $85.00 (cloth); $84.99 (digital). ISBN: 9780198852377.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Law and Religion / Volume 39 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 540-544
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A PROOF OF HIRSCHHORN’S CONJECTURE ON
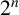 $2^n$-DISSECTION OF EULER’S PRODUCT
$2^n$-DISSECTION OF EULER’S PRODUCT
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 111 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 186-196
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
First report of Leptoglossus occidentalis (Hemiptera: coreidae) feeding on Rubus (Rosaceae) fruit
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 156 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, e25
-
- Article
- Export citation
IMPROVED UPPER BOUNDS ON DIOPHANTINE TUPLES WITH THE PROPERTY
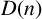 $D(n)$
$D(n)$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 111 / Issue 3 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 428-432
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation