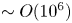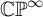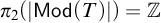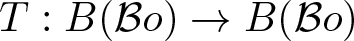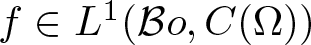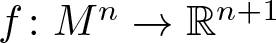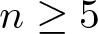Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418087 results in Open Access
Evolution of weak, homogeneous turbulence with rotation and stratification
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, A17
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stochastic modelling of the instantaneous velocity profile in rough-wall turbulent boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, A12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Classifying spaces for families of abelian subgroups of braid groups, RAAGs and graphs of abelian groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 66 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 290-307
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Milena Ivanova and Steven French, The Aesthetics of Science: Beauty, Imagination and Understanding London: Routledge, 2022. Pp. 224. ISBN 978-1-032-33718-0. £110.00 (hardback).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 57 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 125-127
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Turbulent mixing in the vertical magnetic Rayleigh–Taylor instability
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, A8
-
- Article
- Export citation
How Little and Meng’s Objective Approach Fails in Democracies
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 202-207
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Diagnostic stewardship to improve patient outcomes and healthcare-associated infection (HAI) metrics
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 405-411
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Amendments to the Case-Zablocki Act Concerning Reporting and Publication of International Agreements and Related Regulations (U.S.)
-
- Journal:
- International Legal Materials / Volume 63 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 275-300
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Understanding the interplay between sustainability strategy and the approach to sustainability reporting in SMEs
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization / Volume 31 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 1137-1156
-
- Article
- Export citation
Complex Rivalry: The Dynamics of India-Pakistan Conflict. By Surinder Mohan. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 2022. 420p. $85.00 cloth. $39.95 paper.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 924-925
- Print publication:
- September 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
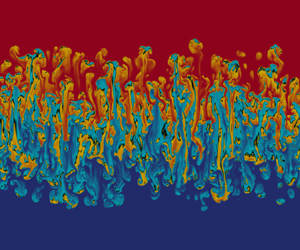
Single cavitation bubble dynamics in a stagnation flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, A18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
NON-TRIVIAL HIGHER HOMOTOPY OF FIRST-ORDER THEORIES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On traces of Bochner representable operators on the space of bounded measurable functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 224-235
-
- Article
- Export citation
What We Do and Do Not Know about Democratic Backsliding
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 224-229
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
BJN volume 131 issue 3 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Infinitesimally Moebius bendable hypersurfaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 236-260
-
- Article
- Export citation
From Railways to Aircraft: Officine Meccaniche Reggiane’s Successful Product Transition in the 1930s
-
- Journal:
- Enterprise & Society / Volume 26 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 170-196
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Goldie dimension for C*-algebras
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 200-223
-
- Article
- Export citation
Volatile States in International Politics. By Eleonora Mattiacci. New York: Oxford University Press, 2023. 232p. $110.00 cloth, $32.00 paper.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 928-930
- Print publication:
- September 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Undead Past: What Drives Support for the Secessionist Goal of the Indigenous People of Biafra (IPOB) in Nigeria?
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Race, Ethnicity and Politics / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, pp. 26-54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation