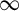Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418034 results in Open Access
RT-SCNNs: real-time spiking convolutional neural networks for a novel hand gesture recognition using time-domain mm-wave radar data
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 16 / Issue 5 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 783-795
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
How to determine a curve singularity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 633-647
- Print publication:
- September 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Case C-663/21, Bundesamt für Fremdenwesen und Asyl v. AA (C.J.E.U.)
-
- Journal:
- International Legal Materials / Volume 63 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 213-225
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Boosted income, busted environment: a tradeoff in the wider economic impacts of transport corridor investments?
-
- Journal:
- Environment and Development Economics / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 107-126
-
- Article
- Export citation
‘… And We have made from water every living thing’: water conservation and the Holy Qur’an
-
- Journal:
- Environmental Conservation / Volume 51 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 79-84
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Democracy, Authoritarianism and Global Economic Governance
-
- Journal:
- Contemporary European History / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 557-568
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inequality or insecurity? The case of pre-colonial farming communities in southern Africa
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
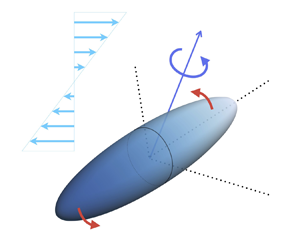
Generalised Jeffery's equations for rapidly spinning particles. Part 1. Spheroids
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, A1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Quaternary climatic events as conditioning factors of hydrogeologic characteristics and salinity in costal aquifers at northern Patagonia, Argentina
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 119 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 152-161
-
- Article
- Export citation
Property, Power, and Imperialism in Angola - Wealth, Land, and Property in Angola: A History of Dispossession, Slavery, and Inequality By Mariana P. Candido. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022. Pp. 288. $110.00, hardcover (ISBN: 9781316511503); $34.99, paperback (ISBN: 9781009055987); $26.00, ebook (ISBN: 9781009052986).
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of African History / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 455-456
-
- Article
- Export citation
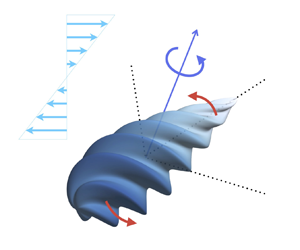
Generalised Jeffery's equations for rapidly spinning particles. Part 2. Helicoidal objects with chirality
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, A2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of different nutrients on blood glucose, inflammatory response and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 1513-1527
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Revisiting the punitiveness of deportation
-
- Journal:
- Legal Studies / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 369-384
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Life history and mitochondrial genomes of Salassinae and Agliinae (Insecta, Lepidoptera): New insights into the loss of cocooning behaviour and phylogeny of Saturniidae
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 107-123
-
- Article
- Export citation
ON MODELLING WATER QUALITY WITH STOCHASTIC DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 65 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 273-284
-
- Article
- Export citation
Flower of Capitalism: South Korean Advertising at a Crossroads By Olga Fedorenko. Honolulu, HI: University of Hawaii Press, 2023, 298 pages. Hardback, $68.00, ISBN: 9780824890346
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Asian Studies / Volume 21 / Issue 2 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 407-410
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rapid generation of time-optimal rendezvous trajectory based on convex optimisation and DNN
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1324 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 1262-1283
-
- Article
- Export citation
ASYMPTOTICS FOR TIME-VARYING VECTOR MA(
 $\infty $) PROCESSES
$\infty $) PROCESSES
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 41 / Issue 3 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 584-616
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Fuzhen Si & Luigi Rizzi (eds.), Current issues in syntactic cartography: A crosslinguistic perspective. Amsterdam/Philadelphia: John Benjamins Publishing Company, 2021. Pp. vi + 327.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Linguistics / Volume 60 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 248-251
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Associations of offspring birthweight and placental weight with subsequent parental coronary heart disease: survival regression using the walker cohort
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 14 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 746-754
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation