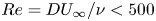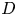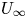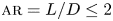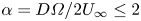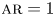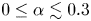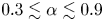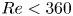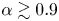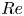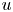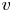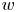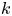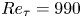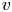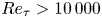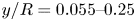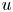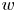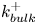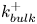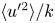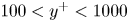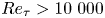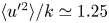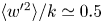Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418667 results in Open Access
Late Quaternary glaciations in the Taniantaweng Mountains
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 117 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 3-18
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Change of Heart, Moral Character and Moral Reform
-
- Journal:
- Kantian Review / Volume 28 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 555-574
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bimbowrieite, NaMgFe3+5(PO4)4 (OH)6⋅2H2O, a new dufrénite-group mineral from the White Rock No.2 quarry, South Australia, Australia
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 88 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 90-96
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mercy and the Construction of Social Control: A Four-Site Analysis of Clemency
-
- Journal:
- Law & Social Inquiry / Volume 49 / Issue 3 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 1812-1841
- Print publication:
- August 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Joshua Grace, African Motors: Technology, Gender, and the History of Development (Durham: Duke University Press, 2021), pp. 432, $30.95 (paperback). ISBN: 9781478011712.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the History of Economic Thought / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 318-320
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
ONTOLOGICAL PURITY FOR FORMAL PROOFS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Review of Symbolic Logic / Volume 17 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 395-434
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A History of Herat: from Chinggis Khan to Tamerlane By Shivan Mahendrarajah. xvi, 379 pp. Edinburgh Studies in Classical Islamic History and Culture, Edinburgh, Edinburgh University Press, 2022.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 263-266
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Los nadies y las nadies: The Effect of Peacebuilding on Political Behavior in Colombia
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Politics and Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 24-51
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Numerical analyses of the flow past a short rotating cylinder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, A15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
TCM volume 20 issue 3 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Twentieth-Century Music / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, p. b1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
GALEN ON HEALTH - (P.N.) Singer (trans.) Galen: Writings on Health. Thrasybulus and Health (De sanitate tuenda). Pp. xxvi + 510, ills. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023. Cased, £120, US$155. ISBN: 978-1-009-15951-7.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 87-88
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Britishness: “Endlessly Coming To An End” - Stuart Ward, Untied Kingdom: A Global History of the End of Britain, (Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2023, 550 p.)
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Sociology / Archives Européennes de Sociologie / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 486-490
-
- Article
- Export citation
A multi-time-scale wall model for large-eddy simulations and applications to non-equilibrium channel flows
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, A51
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contemporary outcomes of aortic arch hypoplasia and coarctation repair in a tertiary paediatric cardiac surgery centre – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, p. 472
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
TCM volume 20 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Twentieth-Century Music / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. f1-f3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Natural Kinds: The Expendables
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Philosophy / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 103-120
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reiterating Hierarchy and the Failed Promise of the Global
-
- Journal:
- Twentieth-Century Music / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 378-401
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of congenital heart disease on mortality and other associated outcomes in children hospitalised for acute asthma exacerbation
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 884-890
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
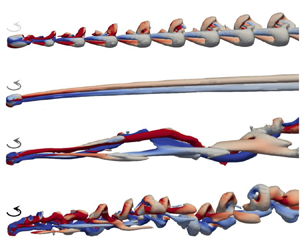
A new propulsion enhancement mechanism in metachronal rowing at intermediate Reynolds numbers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, A45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
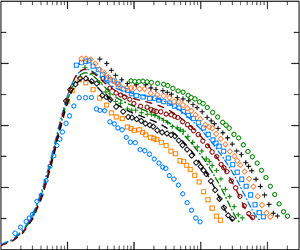
Reynolds number dependence of turbulent kinetic energy and energy balance of 3-component turbulence intensity in a pipe flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, A9
-
- Article
- Export citation