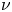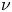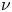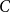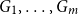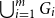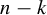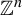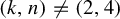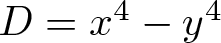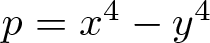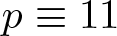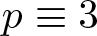Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418669 results in Open Access
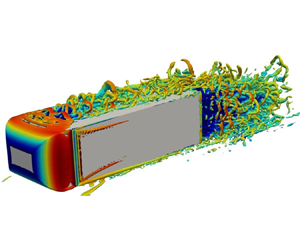
Wake bi-modality: the effect of upstream boundary layer dynamics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, A7
-
- Article
- Export citation
Creative destruction, human capital accumulation, andgrowthin a digital economy
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 28 / Issue 5 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 1206-1230
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pattern evolution and modal decomposition of Faraday waves in a brimful cylinder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, A56
-
- Article
- Export citation
Meditations on ‘international friendship’: Situating twinning in global struggles for solidarity, recognition, and restitution
-
- Journal:
- Review of International Studies / Volume 51 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 375-389
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Three Dogs from the Late Iron Age Boat Grave Cemetery at Gamla Uppsala Prästgården, Sweden
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Archaeology / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 67-84
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Timing of Guilty Pleas: Lessons from Common Law Jurisdictions by Kevin Cheng. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023. 210 pp. Hardcover: US$ 110.00.
-
- Journal:
- Asian Journal of Comparative Law / Volume 19 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 183-184
-
- Article
- Export citation
Letters of challenge: displayed writing, urban public space and honour culture in seventeenth-century Madrid
-
- Journal:
- Urban History / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 79-98
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Metternich's League to Preserve Peace and the Conservative Elites’ Doubts about the Functionality of the Post-Napoleonic Order
-
- Journal:
- Austrian History Yearbook / Volume 55 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 87-102
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
A special case of Vu’s conjecture: colouring nearly disjoint graphs of bounded maximum degree
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 179-195
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Attitude tracking control of hypersonic vehicle based on an improved prescribed performance dynamic surface control
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1323 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 875-895
-
- Article
- Export citation
Integrative analysis of new Clinostomum metacercariae (Digenea, Clinostomidae) using COI mtDNA and morphology rises the number of lineages found in South American freshwater fishes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 97 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, e85
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alexander Linsbichler. Viel mehr als nur Ökonomie: Kopfe und Ideeen der Österreichischen Schule der Nationalökonomie Vienna: Böhlau, 2022. Pp. 278.
-
- Journal:
- Austrian History Yearbook / Volume 55 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 469-471
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Equidistribution of rational subspaces and their shapes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 8 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 2009-2062
- Print publication:
- August 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tone and morphological level ordering in Dagaare
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Notes on Contributors
-
- Journal:
- Twentieth-Century Music / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, p. 273
-
- Article
- Export citation
Variability of Sarocladium oryzae [(Sawada) Games & Hawksworth] and identification of novel donors for sheath rot resistance among temperate germplasm lines of rice
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 349-356
-
- Article
- Export citation
Neolithic Crannogs in the Outer Hebrides (and Beyond?): Synthesis, Survey, and Dating
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society / Volume 89 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 225-247
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A binomial sampling method for estimating the density of blueberry aphid, Ericaphis fimbriata (Hemiptera: Aphididae), in commercial highbush blueberry
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 155 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, e33
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the difference of two fourth powers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 142-150
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nonlinear deterministic reconstruction and prediction of remotely measured ocean surface waves
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, A8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation