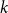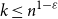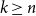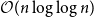Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418609 results in Open Access
Associative plural marking in English varieties: Investigating the expression of group reference
-
- Journal:
- English Today / Volume 40 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 122-126
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Éditorial: La politique du vieillissement et la recherche - des liens mais aussi des énigmes
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 16 / Issue S1 / Spring Printemps 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. ix-xviii
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Linear quadratic approximation of rationally inattentive control problems
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 28 / Issue 6 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 1371-1393
-
- Article
- Export citation
Algorithmic fairness in precision psychiatry: analysis of prediction models in individuals at clinical high risk for psychosis
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 224 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 55-65
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Editorial: Policy and Research on Aging: Connections and Conundrums
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 16 / Issue S1 / Spring Printemps 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. i-viii
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Association between ultra-processed food and flavonoid intakes in a nationally representative sample of the US population
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 1074-1083
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mastermind with a linear number of queries
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 143-156
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
THE SIZE INHERITED AGE EFFECT ON RADIOCARBON DATES OF ALLUVIAL DEPOSITS: REDATING CHARCOAL FRAGMENTS IN A SAND-BED STREAM, MACDONALD RIVER, NSW, AUSTRALIA
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 66 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 1006-1019
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
CJG volume 16 issue S1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 16 / Issue S1 / Spring Printemps 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. f1-f5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Can I Be Honest With My Neurologist? A Problem of Health Technology Assessment in Canada
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 603-605
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Seniors’ Views of Medication Reimbursement Policies: Bridging Research and Policy at the Point of Policy Impact
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 16 / Issue S1 / Spring Printemps 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 114-131
-
- Article
- Export citation
Jennifer Lisa Koslow, Exhibiting Health: Public Health Displays in the Progressive Era New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 2020. Pp. 160. ISBN 978-1-9788-0326-8. $33.95 (paperback).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 57 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 148-150
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Biographies
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 16 / Issue S1 / Spring Printemps 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. xix-xxiv
-
- Article
- Export citation
Shaping Ageing: Social Transformations and Enduring Meanings Adriana Teodorescu and Dan Chiribucă (eds), Routledge, New York, 2022, 196 pp., pbk £38.99, ISBN 13: 9780367495954
-
- Journal:
- Ageing & Society / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 491-493
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Model of Consumer Participation: The Canadian Breast Cancer Initiative
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 16 / Issue S1 / Spring Printemps 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 177-186
-
- Article
- Export citation
Frequency reconfigurable two-element MIMO antenna for cognitive radio and 5G new radio sub-6 GHz applications
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 16 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 295-305
-
- Article
- Export citation
Difference between days of therapy and days of antibiotic spectrum coverage in an inpatient antimicrobial stewardship program: Vector autoregressive models for time-series analysis
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 459-466
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Aging of Aquarius: The Hippies of the 60s in their 60s and Beyond Galit Nimrod, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2023, 277 pp., hbk US $80, ISBN 13: 9781009304078
-
- Journal:
- Ageing & Society / Volume 44 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 739-741
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
AUTHOR INDEX FOR VOLUME 108
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 108 / Issue 3 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 525-528
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Researching multilingually to rethink EMI policy and practices
-
- Journal:
- Language Teaching / Volume 57 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 132-138
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation