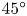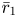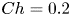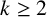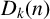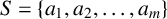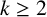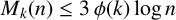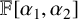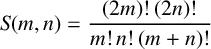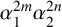Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418543 results in Open Access
Leveraging the developmental neuroscience of caregiving to promote resilience among youth exposed to adversity
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 35 / Issue 5 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 2168-2185
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Becoming a humanitarian state: A performative analysis of ‘status-seeking’ as statecraft in world politics
-
- Journal:
- Review of International Studies / Volume 50 / Issue 4 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 700-719
- Print publication:
- July 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
“Une pièce d’étoffe que nous aurons à faire”: Louis Riel's Utopia: Between Prophecy and Politics
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique / Volume 56 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 917-935
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Power synchronisations determine the hovering flight efficiency of passively pitching flapping wings
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, A41
-
- Article
- Export citation
Large Language Model (LLM)-Powered Chatbots Fail to Generate Guideline-Consistent Content on Resuscitation and May Provide Potentially Harmful Advice
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 757-763
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Franklin Obeng-Odoom. Property, Institutions, and Social Stratification in Africa. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2020. xiii + 364. Figures. Tables. Index. $32.99. Paper. ISBN: 9781108709996.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 190-192
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Capitalism Indivisible
-
- Journal:
- Enterprise & Society / Volume 25 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 39-48
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between the dietary antioxidant index and relative telomere length of leucocytes in the Chinese population
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 1031-1040
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
AN EFFECTIVE BOUND FOR GENERALISED DIOPHANTINE m-TUPLES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 109 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 242-253
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Causal effects of dietary habits on COVID-19 susceptibility, hospitalisation and severity: a comprehensive Mendelian randomisation study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 1007-1014
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of calorie intake and weight gain after Norwood procedure on the outcome of stage II palliation
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 876-883
-
- Article
- Export citation
Peer Versus Pure Benchmarks in the Compensation of Mutual Fund Managers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Volume 59 / Issue 7 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 3101-3138
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
AN ALGEBRAIC INTERPRETATION OF THE SUPER CATALAN NUMBERS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 109 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 498-506
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Anaphoriques en première mention : « Épiphénomène », ou modèle pour le fonctionnement de l’anaphore ?
-
- Journal:
- Journal of French Language Studies / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 205-226
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Physiological and transcriptional status of genetically diverse perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) populations under drought stress
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 331-339
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exponence and the functional load of grammatical tone in Gyeli
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Towards a Public Law Perspective on the Constitutional Law of Privacy in South Africa in the Age of Digitalization
-
- Journal:
- Journal of African Law / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 89-107
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On equivariant topological modular forms
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 159 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 2638-2693
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Horizontal FDI and Internal R&D of Local Firms in Emerging Economies: A Coopetition Perspective
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 981-1004
-
- Article
- Export citation
How do management factors influence digital adoption in the case of a large-scale digital transformation project – A process perspective
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization / Volume 30 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 1564-1584
-
- Article
- Export citation