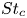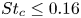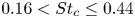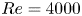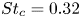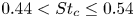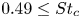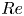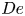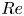Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419516 results in Open Access
On government spending and income inequality under monopolistic competition
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 28 / Issue 6 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 1253-1277
-
- Article
- Export citation
Three-dimensional transition and force characteristics of low-Reynolds-number flows past a plunging airfoil
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, A43
-
- Article
- Export citation
THE METRIC OPERATORS FOR PSEUDO-HERMITIAN HAMILTONIAN
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 65 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 215-228
-
- Article
- Export citation
Long-term effects of physical training on cardiopulmonary exercise parameters in young patients with congenital heart diseases
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 831-837
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The unified extropy and its versions in classical and Dempster–Shafer theories
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 61 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 685-696
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Equivalence and Convention
-
- Journal:
- Philosophy of Science / Volume 91 / Issue 5 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 1242-1250
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Escalating Political Violence and the Intersectional Impacts on Latinas in National Politics
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 238-243
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Instability of a viscoelastic film with insoluble surfactants on an oscillating plane
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, A39
-
- Article
- Export citation
Plant-based diets benefit aerobic performance and do not compromise strength/power performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 5 / 14 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 829-840
- Print publication:
- 14 March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Against Defending Science: Asking Better Questions About Indigenous Knowledge and Science
-
- Journal:
- Philosophy of Science / Volume 91 / Issue 5 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 1210-1220
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investissement
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Yearbook of International Law / Annuaire canadien de droit international / Volume 60 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 268-291
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dispersion with a pinch of salt
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, F1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Analysis and optimisation of mixing in binary droplet collisions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, A38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Framework for the Unsupervised and Semi-Supervised Analysis of Visual Frames
-
- Journal:
- Political Analysis / Volume 32 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 199-220
-
- Article
- Export citation
Distortion element in the automorphism group of a full shift
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 7 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 1757-1817
- Print publication:
- July 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Analytic inclined flow rule for determining granular rheology under strong non-local effects
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, A47
-
- Article
- Export citation
How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Ignore Unwelcome Epistemic Company
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Philosophy / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 121-137
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Feminist Institutionalism in South Africa: Designing for Gender Equality. Edited by Amanda Gouws. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield, 2022. 312 pp. $120.00 (cloth), ISBN: 9781538160084; also available as e-book.
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 775-777
-
- Article
- Export citation
Household Matters: Engendering the Social History of Capitalism
-
- Journal:
- International Review of Social History / Volume 68 / Issue 3 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 483-506
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fluid dynamics in intracranial aneurysms treated with flow-diverting stents: effect of multiple geometrical parameters
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, A45
-
- Article
- Export citation