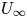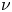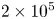Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419563 results in Open Access
Experiment of a thermal plume on an open cylinder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, A6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Selenium status and its determinants in very old adults: insights from the Newcastle 85+ Study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 5 / 14 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, pp. 901-910
- Print publication:
- 14 March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Billionaire Politicians: A Global Perspective
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, pp. 357-371
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparative antimicrobial use in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and non–COVID-19 inpatients from 2019 to 2020: A multicenter ecological study
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, pp. 335-342
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
(D.) LEÃO, (D.) FERREIRA, (N.) SIMÕES RODRIGUES and (R.) MORAIS (eds) Our Beloved Polites: Studies Presented to P.J. Rhodes. Oxford: Archaeopress, 2022. Pp. xiv + 371. £56. 9781803271705.
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Hellenic Studies / Volume 143 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, pp. 361-362
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
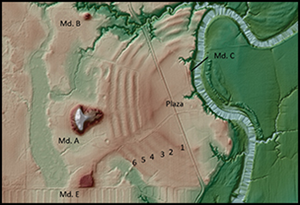
Convergence at Poverty Point: a revised chronology of the Late Archaic Lower Mississippi Valley
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Regulating free speech in a democracy: Lysias 10 Against Theomnestos and the law on slander
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Hellenic Studies / Volume 143 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, pp. 69-85
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exploring high-protein diets in the context of cardiac rehabilitation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 84 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, pp. 75-86
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Explore the Mutual Benefits of Studying the Rights of Sexual Minority People in Hong Kong Confucianism
-
- Journal:
- Social Policy and Society / Volume 23 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, pp. 433-445
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Severe mental illness, race/ethnicity, multimorbidity and mortality following COVID-19 infection: nationally representative cohort study
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 223 / Issue 5 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, pp. 518-525
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
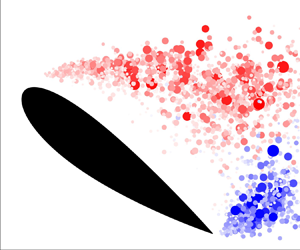
Effects of integral length scale variations on the stall characteristics of a wing at high free-stream turbulence conditions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, A9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A review of physiological measures for mental workload assessment in aviation: A state-of-the-art review of mental workload physiological assessment methods in human-machine interaction analysis
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1323 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, pp. 928-949
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fish oil minimises feed intake and improves insulin sensitivity in Zucker fa/fa rats
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 5 / 14 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, pp. 749-761
- Print publication:
- 14 March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Responsiveness to Coethnics and Cominorities: Evidence from an Audit Experiment of State Legislators
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Race, Ethnicity and Politics / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2023, pp. 55-79
-
- Article
- Export citation
The immigrant versus the state: The marginal contribution of tribunal judges to administrative justice
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Law in Context / Volume 19 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2023, pp. 559-577
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Support to Mitigate the Impact of Suicide for Disaster Aid Workers of the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2023, e517
-
- Article
- Export citation
John F. Mueller The Kaiser, Hitler, and the Jewish Department Store: The Reich's Retailer London: Bloomsbury, 2022. Pp. 256.
-
- Journal:
- Austrian History Yearbook / Volume 55 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2023, pp. 495-497
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Rule-of-Law as a Problem Space: Wāsṭa and the Paradox of Justice in Jordan
-
- Journal:
- Comparative Studies in Society and History / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2023, pp. 131-154
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
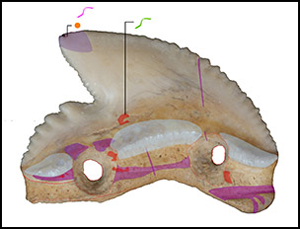
Shark-tooth artefacts from middle Holocene Sulawesi
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The “Is” at Home, the “Ought” Abroad: Self-Comparison as Self-Criticism and the Transylvanian Model in Early Twentieth-Century Romania
-
- Journal:
- Comparative Studies in Society and History / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2023, pp. 213-237
-
- Article
- Export citation