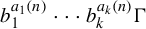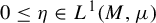Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418748 results in Open Access
Appropriating Memory in the Name of the State
-
- Journal:
- Nationalities Papers / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 225-229
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pointwise convergence in nilmanifolds along smooth functions of polynomial growth
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 7 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 1963-2008
- Print publication:
- July 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stefan Jurasinski and Lisi Oliver, eds. The Laws of Alfred: The “Domboc” and the Making of Anglo-Saxon Law. Studies in Legal History. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021. Pp. 472. $99.99 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 62 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 781-783
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bringing down barriers to children’s healthy eating: a critical review of opportunities, within a complex food system
-
- Journal:
- Nutrition Research Reviews / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 331-351
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
R. C. Richardson. Varieties of History and their Porous Frontiers. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2021. Pp. 232. £61.99 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 62 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 800-802
-
- Article
- Export citation
Edmond Smith. Merchants: The Community that Shaped England's Trade and Empire. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2021. Pp. 376. $32.50 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 62 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 803-805
-
- Article
- Export citation
Gain-enhanced triple-band rectifier-integrated antenna for microwave wireless power transmission
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 16 / Issue 3 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 380-390
-
- Article
- Export citation
(Far) beyond smart specialisation to the foundational economy in Australia?
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 594-609
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mark Bailey. After the Black Death: Economy, Society, and the Law in Fourteenth-Century England. The Ford Lectures for 2019. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2021. Pp. 384. $40.00 (paper).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 62 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 767-768
-
- Article
- Export citation
Social Policy Responses to Rising Inflation in Canada and the United States
-
- Journal:
- Social Policy and Society / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 163-175
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The point of death: Religious conversion and the self in South India
-
- Journal:
- Modern Asian Studies / Volume 58 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 218-242
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lisa Ford. The King's Peace: Law and Order in the British Empire. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2021. Pp. 336. $35.00 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 62 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 775-777
-
- Article
- Export citation
Homeownership rates, housing policies, and co-residence decisions
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 28 / Issue 5 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 1073-1096
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EAP volume 39 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Economics & Philosophy / Volume 39 / Issue 2 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, p. f1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Call for Themed Collections for The Economic and Labour Relations Review
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 629-630
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Jonathan McGovern. The Tudor Sheriff: A Study in Early Modern Administration. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2022. Pp. 315. $100.00 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 62 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 791-792
-
- Article
- Export citation
Driving Irritation: Thailand's Supreme Court and the English Roots of Corporate Criminal Liability
-
- Journal:
- Asian Journal of Comparative Law / Volume 19 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 142-158
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the quasi-ergodicity of absorbing Markov chains with unbounded transition densities, including random logistic maps with escape
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 7 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 1818-1855
- Print publication:
- July 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation