Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418807 results in Open Access
Addressing Violence against Women in Politics: Reflections from an APSA Congressional Fellow
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender / Volume 19 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2023, pp. 950-955
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mixed-reality technology for clinical communication, cocaine screening in patients undergoing nasal reconstructive surgery and prognostic factors for vocal fold leukoplakia
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2023, p. 1063
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Money for Africa and Money in Africa: Colonial Currencies and the Making of Economies and States, 1860s–1960s
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2023, pp. 587-594
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Yellow Star, Red Star: Response to Critiques
-
- Journal:
- Nationalities Papers / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2023, pp. 230-232
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ANZ VOLUME 65 ISSUE 1-2 COVER AND FRONT MATTER
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 65 / Issue 1-2 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Alexander the Great or Būrān-Dukht: who is the true hero of the Dārāb-nāma of Ṭarsūsī?
-
- Journal:
- Iranian Studies / Volume 56 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. 623-636
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
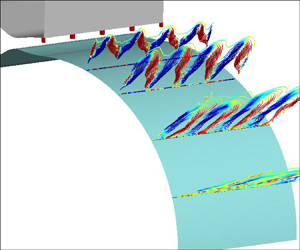
Mixing enhancement of a compressible jet over a convex wall
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, A2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Harmonising and standardising military airworthiness in Europe: a review of key aspects and achievements
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1323 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. 911-927
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Conservation and indigenous peoples’ struggles for livelihoods: Suba Park (Ethiopia)
-
- Journal:
- Environmental Conservation / Volume 50 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. 251-258
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pressure plateau of separation induced by shock impingement in a Mach 5 flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, R1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Informal third-party actors in street-level welfare decisions: a case study of Pakistan social assistance
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Social Policy / Volume 54 / Issue 3 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. 811-828
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Intersections of phenomenology, voice beliefs and distress in bipolar disorder: a comparison with schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. 78-92
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Shock-induced atomisation of a liquid metal droplet
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, A7
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research on “native” and “non-native” English-speaking teachers: Past developments, current status, and future directions
-
- Journal:
- Language Teaching / Volume 57 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. 1-41
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Detecting cognitive decline in high-functioning older adults: The relationship between subjective cognitive concerns, frequency of high neuropsychological test scores, and the frontoparietal control network
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. 220-231
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exploring the Connections between Confidence in the Digital/Online Future and Changes in Anglican Clergy Psychological Well-being during the Third Covid Lockdown in England during 2021
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Anglican Studies / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. 109-129
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dawn M. Nothwehr, OSF, Franciscan Writings – Hope Amid Ecological Sin and Climate Emergency. London, T & T Clark. 2023. pp. 336. Pbk. ISBN 9780567699145. £21.99.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Anglican Studies / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. 613-614
-
- Article
- Export citation
Adaptive preferences, self-expression and preference-based freedom rankings
-
- Journal:
- Economics & Philosophy / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. 513-534
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Jessica Gabriel Peritz, The Lyric Myth of Voice: Civilizing Song in Enlightenment Italy (Oakland: University of California Press, 2022). xi + 282 pp. $65.00, £55.00
-
- Journal:
- Nineteenth-Century Music Review / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. 138-143
-
- Article
- Export citation
The origins of scientific Buddhism in nineteenth-century Thai intellectual thought
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Southeast Asian Studies / Volume 54 / Issue 3 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, pp. 389-418
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation