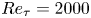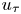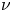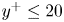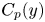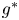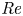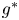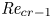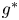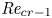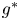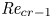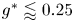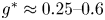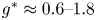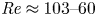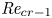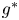Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418918 results in Open Access
AQY volume 97 issue 395 Cover and Back matter
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Two early layers of Sanctus melodies
-
- Journal:
- Plainsong & Medieval Music / Volume 32 / Issue 2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, pp. 131-146
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Introduction: New Approaches to Music and Sound
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of the Gilded Age and Progressive Era / Volume 22 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, pp. 367-383
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ANT volume 103 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- The Antiquaries Journal / Volume 103 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 December 2023, pp. f1-f6
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Visions of the Roman North: art and identity in northern Roman Britain. By Iain Ferris. 245mm. Pp 230, 107 figs (mostly col). Archaeopress Roman Archaeology 80, Archaeopress, Oxford, 2021. isbn 9781789699050. £35 (pbk).
-
- Journal:
- The Antiquaries Journal / Volume 103 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 442-443
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Kaleidoscope
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 223 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 497-498
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Contributors
-
- Journal:
- Popular Music / Volume 42 / Issue 3 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. i-ii
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Catherine Saucier, ed., Historia sancti Iohannis evangeliste (traditionibus Leodiensis et Boscudocis), Wissenschaftliche Abhandlungen/Musicological Studies 65, Historiae 34. Kitchener, ON: The Institute of Mediæval Music, 2021. lxi + 41 pp. €120. ISBN 978 1 926664 60 6.
-
- Journal:
- Plainsong & Medieval Music / Volume 32 / Issue 2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, pp. 167-169
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Editor's Note
-
- Journal:
- Iranian Studies / Volume 56 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2023, p. 613
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Editor's note
-
- Journal:
- Art Libraries Journal / Volume 48 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 October 2023, p. 91
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Staffordshire Hoard: an Anglo-Saxon treasure. Edited by Chris Fern, Tania Dickinson and Leslie Webster, Pp xxxv + 586, 314 figs, 32 tabs. Research Report of the Society of Antiquaries of London 80, Society of Antiquaries of London, London, 2019. isbn 9781527233508. £49.95 (hbk).
-
- Journal:
- The Antiquaries Journal / Volume 103 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 444-448
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sir Edward Carne of Ewenni, c.1496-1561 — CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- British Catholic History / Volume 36 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2023, p. 481
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
EMH volume 42 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Early Music History / Volume 42 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2025, p. b1
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
E-band backhaul antenna for fine beam alignment
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 16 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. 30-40
-
- Article
- Export citation
Flow dynamics in sinusoidal channels at moderate Reynolds numbers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, A22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Taylor's frozen hypothesis of the pressure fluctuations in turbulent channel flow at high Reynolds numbers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, A15
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dynamics of unionism in the platform economy: the case of the food delivery sector in Bologna, Italy
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. 395-412
-
- Article
- Export citation
LEA—A NOVEL LOW ENERGY ACCELERATOR FOR 14C DATING
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 66 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. 1280-1288
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WHEN LIBERTY PRESUPPOSES ORDER: F. A. HAYEK’S CONTEXTUAL ORDOLIBERALISM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the History of Economic Thought / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. 288-311
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Three-dimensional wake transitions of steady flow past two side-by-side cylinders
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, A17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation