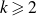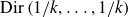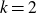Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419635 results in Open Access
Trajectories of crop–livestock integration in the context of specialization in Northwest Vietnam
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 161 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 488-501
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dirichlet law for factorisation of integers, polynomials and permutations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 175 / Issue 3 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 649-676
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Revisiting “Racial Capitalism”
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Sociology / Archives Européennes de Sociologie / Volume 64 / Issue 2 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 173-181
-
- Article
- Export citation
High consumption of dairy products and risk of major adverse coronary events and stroke in a Swedish population
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 500-511
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Confederal Union and Empire: Placing the Albany Plan (1754) in Imperial Context
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 62 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 589-617
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Scato-sexual Message: The Secundinus Stone with Phallus from Vindolanda
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A new probability density function for the surface elevation in irregular seas
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 970 / 10 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, A38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Shear dispersion of multispecies electrolyte solutions in the channel domain
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 970 / 10 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, A27
-
- Article
- Export citation
OPTIMAL GEVREY STABILITY OF HYDROSTATIC APPROXIMATION FOR THE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS IN A THIN DOMAIN
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 23 / Issue 4 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 1521-1566
- Print publication:
- July 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
A retrospective analysis: follow up with 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography in oro- and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma patients
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 7 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 747-754
- Print publication:
- July 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An approximation formula for the shifted cubic moment of automorphic L-functions in the weight aspect
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 77 / Issue 3 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 715-738
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Issue on Opera and Ancient Sources in the Nineteenth Century
-
- Journal:
- Nineteenth-Century Music Review / Volume 21 / Issue 2 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 208-212
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Phenotypic characterization of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) revealed promising genotypes for moisture stress conditions
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 218-228
-
- Article
- Export citation
ROB volume 41 issue 10 Cover and Front matter
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Sex and age group differences in the intakes and dietary sources of vitamin B12 in nationally representative samples of children (5–12y) and teenagers (13–18y) in Ireland
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2023, E255
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Th17 response following in vitro exposure to mercury with and without n-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients compared to healthy controls
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2023, E265
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Le conseguenze economiche delle leggi razziali by Ilaria Pavan, Bologna, Il Mulino, 2022, 320 pp., €25 (paperback), ISBN 9788815295002
-
- Journal:
- Modern Italy / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2023, pp. 238-240
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Border Carbon Adjustments: Should Production or Consumption be Taxed?
-
- Journal:
- World Trade Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3-4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2023, pp. 395-407
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dangerous Deception: Hoax Improvised Explosive Devices and their Impact on Prehospital Medical Care During Terrorist Attacks
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2023, pp. 693-695
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation