Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1417116 results in Open Access
Review of Parenting Twins: The Adventure Begins by Elizabeth A. Stewart
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 28 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, p. 111
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hand hygiene opportunities in neonatal intensive care: a multicenter observational study to calibrate group electronic monitoring systems
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 46 / Issue 5 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 551-553
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Risk of late sudden death after surgery for congenital heart disease
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 805-811
-
- Article
- Export citation
Room-temperature X-ray powder diffraction data for bosentan monohydrate
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 40 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 146-156
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Differential associations between birthweight and cardiometabolic characteristics among persons with and without type 2 diabetes in the UK Biobank
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 16 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Corpus linguistics for language teaching and learning: A research agenda
-
- Journal:
- Language Teaching / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 232-251
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Transition of solitary waves and undular bore from basin to channel with opposing current
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1006 / 10 March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, A1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Global corn area from 1960 to 2030: patterns, trends and implications
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 163 / Issue 3 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 295-306
-
- Article
- Export citation
NOTE ON A DYNAMICAL GENERALISATION OF THE PRIME NUMBER THEOREM FOR ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Low-order kaolinite from bauxite mine tailings in the Amazon as a precursor for geopolymers: mineralogical and mechanical properties
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 73 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, e6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Calibration and bias correction of seasonal weather forecasts from the North American Multi-Model Ensemble: Potential applications for regional crop modelling and irrigation management
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 163 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 145-159
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mini-invasive surgical approach for hybrid pulmonary valve implantation: an option for very high-risk patients
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 845-849
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Crystal structure of diroximel fumarate, C11H13NO6
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 40 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 140-145
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High prevalence of multidrug-resistant bacteria on patient medical file surfaces at five critical care units in Kampala, Uganda: an explanatory sequential mixed-methods study
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 46 / Issue 5 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 554-556
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
LONGEST CYCLES AND LONGEST CHORDLESS CYCLES IN
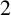 $2$-CONNECTED GRAPHS
$2$-CONNECTED GRAPHS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
The significance of feathers in early and medieval China
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies / Volume 88 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 223-241
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Towards the decipherment of Thamudic D: an identification of new glyphs and phoneme values
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies / Volume 88 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 195-222
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Carbon pricing and household welfare: Evidence from Uganda-Erratum
-
- Journal:
- Environment and Development Economics / Volume 30 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, p. 176
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A quote attributed to Udbhaṭabhaṭṭa, which is actually from Arcaṭa
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies / Volume 88 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 331-345
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Illicit trafficking in cultural property as a human rights issue: Sovereignty over cultural resources and the right to self-determination. Case study of Iraq
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Cultural Property / Volume 32 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 31-57
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation