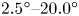Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418748 results in Open Access
Mechanisms of exercise-related neurocardiogenic syncope and the relationship between resting and dynamic cardiac testing
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2025, pp. 399-406
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dynamics of solitary waves on a ferrofluid jet: the Hamiltonian framework
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1002 / 10 January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2025, A23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Asymptotics for crank of overpartitions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2025, pp. 1-34
-
- Article
- Export citation
Restoration of legacy contaminated sites in Antarctica: Lessons from Vanda Station, McMurdo Dry Valleys
-
- Journal:
- Polar Record / Volume 61 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2025, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Molecular characterisation and expression profiles of an odorant-binding proteins gene (FoccOBP9) from Frankliniella occidentalis
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 115 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2025, pp. 74-83
-
- Article
- Export citation
Internal migration in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia): variations across economic zones in 2006–2023
-
- Journal:
- Polar Record / Volume 61 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2025, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The added value of metadata on test completion time for the quantification of cognitive functioning in survey research
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 31 / Issue 2 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2025, pp. 117-126
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
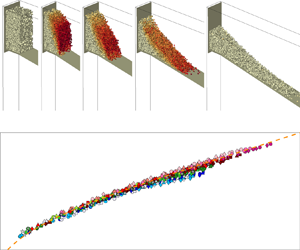
Run-out scaling of granular column collapses on inclined planes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1002 / 10 January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2025, A50
-
- Article
- Export citation
Our lives go better in a world created by God
-
- Journal:
- Religious Studies / Volume 61 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 350-364
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dichotomy spectrum and reducibility for mean hyperbolic systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stefan Heid, Altar and Church: Principles of Liturgy from Early Christianity (Regensburg: Schnell und Steiner; Washington, D.C.: The Catholic University of America Press, 2023)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Anglican Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spinal Intramedullary Abscess of Blastomycosis Etiology in an Immunocompetent 19-Year-Old Male
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 52 / Issue 5 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 876-879
-
- Article
- Export citation
Age and anxiety symptoms jointly moderated the curvilinear changes in trial-level ERN following repeated errors on a Go/No-Go task during early adolescence
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Learned Societies, Knowledge Production, and Public Engagement in Colonial and Postcolonial Ghana, 1930–90
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of African History / Volume 65 / Issue 3 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 381-397
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Generalized torsion orders and Alexander polynomials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 68 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 401-420
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Biderivations of Lie algebras
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 68 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 440-450
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
High takeoff of the right coronary artery by echocardiography: normal variant or something more?
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 35 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 32-37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Divorce Petitions by Trafficked Women Denied: Legal Consciousness, Circuit of Commerce and the State
-
- Journal:
- Asian Journal of Law and Society / Volume 12 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 22-39
-
- Article
- Export citation
Assessing neighbourhood-scale BTI spray applications and laboratory-based mortality testing on Aedes aegypti larval development
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 115 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 56-65
-
- Article
- Export citation
Neurosteroid replacement therapy using tiagabine and zuranolone restores cerebellar neurodevelopment and reduces hyperactive behaviour following preterm birth
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 16 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation