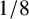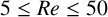Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1417613 results in Open Access
Analysing policy gaps in protecting avian species from electrocution and power-line collision in Kenya
-
- Journal:
- Environmental Conservation / Volume 51 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 290-294
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Long induced paths in expanders
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 276-282
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Strategic responses to anti-DEI legislation: The promise of culturally responsive assessments
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 481-485
-
- Article
- Export citation
Minding the gap: Mindful inclusion of opposing perspectives to protect DEI initiatives
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 490-494
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Values and facts and fancies
-
- Journal:
- Religious Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
FURTHER ACCURACY VERIFICATION OF A 2D ADAPTIVE MESH REFINEMENT METHOD USING STEADY FLOW PAST A SQUARE CYLINDER
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 67 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
We need to find out where small businesses find information first
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 430-433
-
- Article
- Export citation
A panel discussion on addressing the science–practice gap with academic–industry collaborations
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 402-405
-
- Article
- Export citation
Justice without millionaires
-
- Journal:
- Economics & Philosophy / Volume 41 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 186-187
-
- Article
- Export citation
Beth Singler Religion and Artificial Intelligence: An Introduction(New York: Routledge, 2025). pp. 1–217. £35.99 (Pbk). ISBN 9781032187648
-
- Journal:
- Religious Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Industrial-organizational psychology research is useful for small businesses
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 449-451
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On statistical zonostrophic instability and the effect of magnetic fields
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 999 / 25 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, A77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Noisy group testing via spatial coupling
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 210-258
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Let me in: Building an I-O bridge that combats the subtle redlining of the scientist–practitioner gap
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 406-411
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PSA volume 91 issue 5 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Philosophy of Science / Volume 91 / Issue 5 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. f1-f6
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Counteracting threats to DEI with good trouble and innovation
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 495-498
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Transforming Africa’s food systems: building resilience to deliver healthy diets
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bidirectional relation of self-regulation with oppositional defiant disorder symptom networks and moderating role of gender
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 37 / Issue 3 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 1616-1627
-
- Article
- Export citation
News Sharing on Social Media: Mapping the Ideology of News Media, Politicians, and the Mass Public
-
- Journal:
- Political Analysis / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 73-90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation