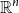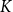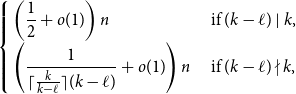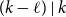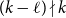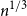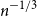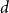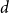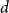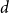Refine search
Actions for selected content:
6950 results in Algorithmics, Complexity, Computer Algebra, Computational Geometry
Partial recovery and weak consistency in the non-uniform hypergraph stochastic block model
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2024, pp. 1-51
-
- Article
- Export citation
The full rank condition for sparse random matrices
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 643-707
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The List-Ramsey threshold for families of graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 829-851
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A new formula for the determinant and bounds on its tensor and Waring ranks
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 769-794
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the Ramsey numbers of daisies I
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 795-806
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the Ramsey numbers of daisies II
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 742-768
-
- Article
- Export citation
List packing number of bounded degree graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 807-828
-
- Article
- Export citation
Counting spanning subgraphs in dense hypergraphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2024, pp. 729-741
-
- Article
- Export citation
A generalisation of Varnavides’s theorem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 May 2024, pp. 724-728
-
- Article
- Export citation
Noise sensitivity of the minimum spanning tree of the complete graph
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2024, pp. 708-723
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rainbow Hamiltonicity in uniformly coloured perturbed digraphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2024, pp. 624-642
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

Online Algorithms
-
- Published online:
- 07 May 2024
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2023
Maximum chordal subgraphs of random graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 May 2024, pp. 611-623
-
- Article
- Export citation
Turán problems in pseudorandom graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, pp. 583-596
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Central limit theorem for components in meandric systems through high moments
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, pp. 597-610
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Behaviour of the minimum degree throughout the
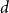 ${\textit{d}}$-process
${\textit{d}}$-process
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, pp. 564-582
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A generalization of Bondy’s pancyclicity theorem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 554-563
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The distribution of the maximum protection number in simply generated trees
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 4 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 518-553
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Algorithms for the ferromagnetic Potts model on expanders
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 4 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2024, pp. 487-517
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dedication
-
- Book:
- Polytopes and Graphs
- Published online:
- 14 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 21 March 2024, pp v-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation