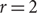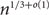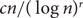Refine search
Actions for selected content:
48464 results in Computer Science
Typed dataspace actors
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Functional Programming / Volume 30 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, e27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A CLASS OF SMALL DEVIATION THEOREMS FOR FUNCTIONALS OF RANDOM FIELDS ON A TREE WITH UNIFORMLY BOUNDED DEGREE IN RANDOM ENVIRONMENT
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, pp. 169-183
-
- Article
- Export citation
Elastic sheet-defined functions: Generalising spreadsheet functions to variable-size input arrays
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Functional Programming / Volume 30 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 August 2020, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Cluster-based mention typing for named entity disambiguation
-
- Journal:
- Natural Language Engineering / Volume 28 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2020, pp. 1-37
-
- Article
- Export citation
Simplifying the Measurement of Attitudes towards Autistic People
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2020, e29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Computational Model for Estimating the Progression of COVID-19 Cases in the US West and East Coast Population Regions
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2020, e41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Calculating correct compilers II: Return of the register machines
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Functional Programming / Volume 30 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2020, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Framing bullying as a health risk: Null effects on young adults’ support for anti-bullying policies
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2020, e27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Breaking bivariate records
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2020, pp. 105-123
-
- Article
- Export citation
Public awareness of tetralogy of Fallot after Jimmy Kimmel Live! television episode: A cross-sectional analysis
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2020, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cyclopentadithiophene polymers synthesised via Suzuki-Miyaura polymerisation of MIDA boronate esters
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2020, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Monochromatic cycle partitions in random graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2020, pp. 136-152
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Many disjoint triangles in co-triangle-free graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2020, pp. 153-162
-
- Article
- Export citation
Toward an interdisciplinary integration between multi-agents systems and multi-robots systems: a case study
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Knowledge Engineering Review / Volume 35 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2020, e35
-
- Article
- Export citation
Improved Ramsey-type results for comparability graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 29 / Issue 5 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2020, pp. 747-756
-
- Article
- Export citation
A low-power prototype of contactless field power controlled BLAC and BLDC motors
-
- Journal:
- Wireless Power Transfer / Volume 7 / Issue 2 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2020, pp. 106-115
- Print publication:
- September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
ROB volume 38 issue 9 Cover and Back matter
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ROB volume 38 issue 9 Cover and Front matter
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation