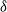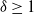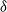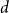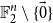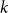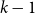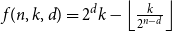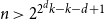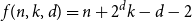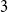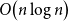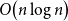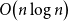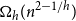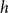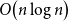Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52650 results in Statistics and Probability
Averaging for slow–fast piecewise deterministic Markov processes with an attractive boundary
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, pp. 1439-1468
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Raw driving data of passenger cars considering traffic conditions in Semnan city
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prediction of the COVID-19 transmission: a case study of Pakistan
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, e89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Development and external validation of a prognostic tool for nonsevere COVID-19 inpatients
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, e128
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Kalikow decomposition for counting processes with stochastic intensity and application to simulation algorithms
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, pp. 1469-1500
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Use of portable air purifiers to reduce aerosols in hospital settings and cut down the clinical backlog: a critical analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, e86
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Distributions of random variables involved in discrete censored δ-shock models
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 55 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, pp. 1144-1170
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
TESTING FOR ANTICIPATED CHANGES IN SPOT VOLATILITY AT EVENT TIMES
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 41 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, pp. 1-34
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association of current hepatitis B virus infection with mortality in adults with sepsis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, e94
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Joint models for cause-of-death mortality in multiple populations
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Actuarial Science / Volume 18 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2023, pp. 51-77
-
- Article
- Export citation
Subspace coverings with multiplicities
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2023, pp. 782-795
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genetic and epidemiological analyses of infection load and its relationship with psychiatric disorders
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2023, e93
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A pair degree condition for Hamiltonian cycles in 3-uniform hypergraphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2023, pp. 762-781
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Intergenerational risk sharing in a defined contribution pension system: analysis with Bayesian optimization
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 53 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2023, pp. 515-544
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Neural networks for quantile claim amount estimation: a quantile regression approach
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Actuarial Science / Volume 18 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2023, pp. 30-50
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A NOVEL APPROACH TO PREDICTIVE ACCURACY TESTING IN NESTED ENVIRONMENTS
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 41 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2023, pp. 35-78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Universal geometric graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2023, pp. 742-761
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An investigation of the seasonal relationships between meteorological factors, water quality, and sporadic cases of Legionnaires’ disease in Washington, DC
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2023, e88
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exponential control of the trajectories of iterated function systems with application to semi-strong GARCH
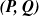 $\boldsymbol{{(P, Q)}}$ models
$\boldsymbol{{(P, Q)}}$ models
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2023, pp. 1501-1515
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Adverse childhood experiences and craving: Results from an Italian population in outpatient addiction treatment
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 May 2023, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation