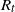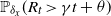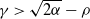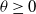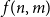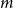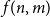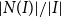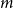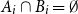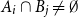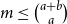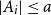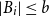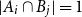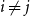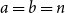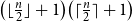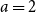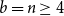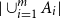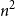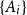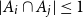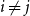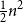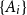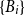Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52650 results in Statistics and Probability
SIR epidemics driven by Feller processes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2023, pp. 1293-1316
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
The virtuous smart city: Bridging the gap between ethical principles and practices of data-driven innovation
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2023, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A large deviation theorem for a supercritical super-Brownian motion with absorption
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2023, pp. 1249-1274
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Maximal chordal subgraphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2023, pp. 724-741
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Estimating the VaR-induced Euler allocation rule
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 53 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2023, pp. 619-635
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prevalence of respiratory pathogens and risk of developing pneumonia under non-pharmaceutical interventions in Suzhou, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2023, e82
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON THE SIZE CONTROL OF THE HYBRID TEST FOR SUPERIOR PREDICTIVE ABILITY
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2023, pp. 213-232
-
- Article
- Export citation
ASB volume 53 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 May 2023, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ASB volume 53 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 May 2023, pp. b1-b3
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Mandatory and seasonal vaccination against COVID-19: Attitudes of the vaccinated people in Serbia
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2023, e83
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exploring the effect of novel six moments on hand hygiene compliance among hospital cleaning staff members: a quasi-experimental study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2023, e73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effectiveness of near-UVA in SARS-CoV-2 inactivation
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2023, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Circulation and colonisation of Blastocystis subtypes in schoolchildren of various ethnicities in rural northern Thailand
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2023, e77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mixing time bounds for edge flipping on regular graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2023, pp. 1317-1332
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Uniform-in-phase-space data selection with iterative normalizing flows
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2023, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Approaching the coupon collector’s problem with group drawings via Stein’s method
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2023, pp. 1352-1366
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ramsey upper density of infinite graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2023, pp. 703-723
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prevalence of Trypanosoma cruzi infection in a cohort of people living with HIV/AIDS from an urban area
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2023, e72
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
INTERCEPT ESTIMATION IN NONLINEAR SELECTION MODELS
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 40 / Issue 6 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 1311-1363
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Problems and results on 1-cross-intersecting set pair systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 691-702
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation