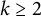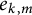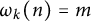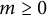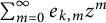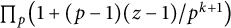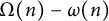Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419572 results in Open Access
Sustainability of a customized electronic duplicate order alert for microbiology tests: assessment of alert fatigue 12 to 36 months after implementation
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 46 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 110-111
- Print publication:
- January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Beyond Changing Minds: Raising the Issue Importance of Expanding Legal Immigration
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multi-granularity onboard decision method for optical space surveillance satellite
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 129 / Issue 1334 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 975-1000
-
- Article
- Export citation
Antimicrobial-resistant central line-associated bloodstream infections in adult intensive care units: findings from an Australian surveillance network, 2011–2022
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 12 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1378-1384
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Word of mouth: Mouthing patterns in a bimodal multilingual deaf community
-
- Journal:
- Language in Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Do anomalous aortic origin of a coronary artery patients have higher risk of myocardial ischaemia and adverse cardiac events during aortic and mitral valve replacements?
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 10 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 2086-2093
-
- Article
- Export citation
FUNCTIONAL INSTRUMENTAL VARIABLE REGRESSION WITH AN APPLICATION TO ESTIMATING THE IMPACT OF IMMIGRATION ON NATIVE WAGES
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1-36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Maternal under-nutrition during pregnancy alters the molecular response to over-nutrition in multiple organs and tissues in nonhuman primate juvenile offspring
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 15 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, e27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Morphology in action: Diminutives in Brazilian obstetric and gynecological consultations
-
- Journal:
- Language in Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1-32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Significance of Small Things: Small Hydropower in the People’s Republic of China, 1949–1983
-
- Journal:
- Comparative Studies in Society and History / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 141-168
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
History in the plural: Reconfigurations of past–present–future
-
- Journal:
- Review of International Studies / Volume 51 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 357-374
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using liberal–legal tools for illiberal gains: the European Court of Human Rights and legal mobilisation by conservative right-wing actors
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Law in Context / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 401-418
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
JPR volume 61 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 61 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Perceiving God like an angel
-
- Journal:
- Religious Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Distribution of the number of prime factors with a given multiplicity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1107-1122
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Calcium plus vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy has no impact on postpartum transient longitudinal changes in hip geometry in adolescent mothers: a secondary analysis of a randomised controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 132 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 1325-1333
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
“It's Not Our Responsibility, But We Need to Do Something”: Explaining Local Government Responses to the Homelessness and Housing Crises
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique / Volume 57 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 763-768
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
How conservative groups fight liberal values and try to ‘moralize’ the European Court of Human Rights
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Law in Context / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 360-378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation