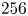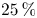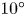Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419572 results in Open Access
Reconfigurable cable-driven parallel mechanism design: physical constraints and control
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exploring Comorbidity Between Anxiety and Depression in Spanish-Speaking School-Aged Children: A Network Analysis Approach
-
- Journal:
- The Spanish Journal of Psychology / Volume 27 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, e27
-
- Article
- Export citation
Benjamin Labatut, The MANIAC New York: Penguin, 2023. Pp. 368. ISBN 978-0-593-65447-7. $28.00 (hardcover).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, pp. 367-368
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multiplexed gastrointestinal PCR panels for the evaluation of diarrhea in patients with acute leukemia
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 46 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, pp. 77-80
- Print publication:
- January 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ethical entanglements: human remains, museums and ethics in a European perspective
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Expansion of the critical intensity for the random connection model
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, pp. 158-209
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Schizophrenia – new treatments soon
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 226 / Issue 3 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, pp. 127-128
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Disentangling the gender-differentiated determinants of home-based self-employment choices in Nigeria
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, pp. 905-938
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
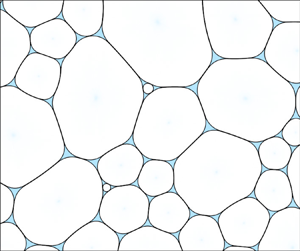
Effects of liquid fraction and contact angle on structure and coarsening in two-dimensional foams
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 999 / 25 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, A10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Labour market segmentation, self-employment, and Hukou reform
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review / Volume 35 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, pp. 730-748
-
- Article
- Export citation
Questionnaire Survey on Stockpiling Medicines for Disasters in Pharmacies in Gifu City in Anticipation of Nankai Trough Earthquake
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, e259
-
- Article
- Export citation
LARGE GLOBAL VOLATILITY MATRIX ANALYSIS BASED ON OBSERVATION STRUCTURAL INFORMATION
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the short-wavelength three-dimensional instability in the cylinder wake
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 999 / 25 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, A13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Notification, Viewing the Body, and Social and Cultural Considerations After Traumatic Death: A Systematic Literature Review
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, e256
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Legacy of Ann Cyphers for Olmec Archaeology: Ann Cyphers (1950–2023)
-
- Journal:
- Ancient Mesoamerica / Volume 35 / Issue 3 / Fall 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, pp. 997-1002
- Print publication:
- Fall 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Popugaevaite, Ca3[B5O6(OH)6]FCl2·8H2O, a new phylloborate mineral
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 89 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, pp. 225-233
-
- Article
- Export citation
William C. Summers, The American Phage Group: The Founders of Molecular Biology New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 2023. Pp. 312. ISBN 978-0-300-26356-5. $65.00 (hardcover).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, pp. 369-370
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
New data about the use of coinage in Late Antique Tridentum (Trento, Italy)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Roman Archaeology / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2024, pp. 557-586
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation