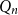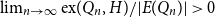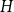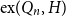Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1416829 results in Open Access
Letting the Lark Ascend: Vaughan Williams's ‘Most Popular Work’ and the Limits of Revisionism
-
- Journal:
- Nineteenth-Century Music Review / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 550-573
-
- Article
- Export citation
Trait anxiety predicting the developmental trajectories of depression symptoms in children: The mediating role of attentional control
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 633-644
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ETS volume 44 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ETS volume 44 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PRM volume 154 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Don’t Call It a Failure: Systemic Risk Governance for Complex Financial Systems
-
- Journal:
- Law & Social Inquiry / Volume 49 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 2245-2286
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Michael Wahman. Controlling Territory, Controlling Voters: The Electoral Geography of African Campaign Violence. New York: Oxford University Press, 2024. 272 pp. $90. Hardcover. ISBN: 9780198872825.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 67 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 722-723
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Power and Identity at the Margins of the Ancient Near East. 2023. Sara Mohr and Shane M. Thompson, editors. University Press of Colorado, Denver. xiv + 205 pp. $63.00 (hardcover), ISBN 978-1-64642-357-6. $50.00 (e-book), ISBN 978-1-64642-358-3.
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 89 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 334-335
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Distribution of growth lines in the tube wall of serpulids (Polychaeta, Annelida)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Constitutive Power of Public Debate
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique / Volume 57 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 156-173
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
János Imre Heltai & Eszter Tarsoly (eds.), Translanguaging for equal opportunities: Speaking Romani at school. Berlin: De Gruyter Mouton, 2023. Pp. 321. eBook Open Access, Hb. €115.
-
- Journal:
- Language in Society / Volume 53 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 552-555
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impact of obstructive sleep apnoea on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in young adults with congenital heart anomalies: insights from the national inpatient sample (2019)
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 7 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 1466-1470
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impact of Automated Prognostication on Traumatic Brain Injury Care: A Focus Group Study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 819-827
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sam Girling, ed., Pierre Rode: Selected String Quartets, Recent Researches in the Music of the Nineteenth and Early Twentieth Century, vol. 87. Middleton, WI: A-R Editions, 2023, xxi, 162 pp. $250.00.
-
- Journal:
- Nineteenth-Century Music Review / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 604-607
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impact of universal chlorhexidine bathing with or without COVID-19 intensive training on staff and resident COVID-19 case rates in nursing homes
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 7 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 906-909
- Print publication:
- July 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Accounting for Carbon Pricing in Third Countries Under the EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism
-
- Journal:
- World Trade Review / Volume 23 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 169-189
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sinus venosus atrial septal defect presenting with platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome in the setting of COVID-19 infection
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 1139-1141
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A class of graphs of zero Turán density in a hypercube
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 404-410
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
IDEMPOTENT GENERATORS OF INCIDENCE ALGEBRAS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 110 / Issue 3 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 488-497
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation