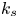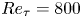Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418748 results in Open Access
Wettability effect on displacement in disordered media under preferential flow conditions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, A33
-
- Article
- Export citation
THE ANECDOTE IN CICERO - (M.) Grandl Ciceroniana. Zur anekdotischen Strategie in Ciceros rhetoriktheoretischen und philosophischen Schriften. (Episteme in Bewegung 27.) Pp. xii + 401. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz, 2022. Cased, €89. ISBN: 978-3-447-11811-8.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 101-104
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Victoria Tkaczyk, Thinking with Sound: A New Program in the Sciences and Humanities around 1900 Chicago: The University of Chicago Press, 2023. Pp. 304. ISBN 978-0-226-82328-7. $55.00 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 57 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 129-131
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
LIVED ANCIENT RELIGION IN THE ROMAN EMPIRE - (J.) Rüpke, (G.) Woolf (edd.) Religion in the Roman Empire. (Die Religionen der Menschheit 16.2.) Pp. 323, ills, maps. Stuttgart: Kohlhammer, 2021. Cased, €89. ISBN: 978-3-17-029224-6.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 279-281
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Community-Based Nutrition Risk Screening in Older Adults (COMRISK): An Exploration of the Experience of Being Screened and Prevalence of Nutrition Risk in Alberta, Canada
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 43 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 385-395
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Leibniz's Moral Psychology of an Evil Person
-
- Journal:
- Dialogue: Canadian Philosophical Review / Revue canadienne de philosophie / Volume 64 / Issue 2 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 377-399
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparison of different PCR amplification targets for molecular diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 97 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, e88
-
- Article
- Export citation
Latest Topics of Interest on Radiation Risk Communication: A Decade After Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant Accident
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, e531
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Infant gut microbiota and negative and fear reactivity
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 36 / Issue 4 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 2016-2031
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prediction of equivalent sand-grain size and identification of drag-relevant scales of roughness – a data-driven approach
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, A34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Functional improvements associated with cranioplasty after stroke and traumatic brain injury: a cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Brain Impairment / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 721-731
-
- Article
- Export citation
Optimal performance of a tontine overlay subject to withdrawal constraints
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 54 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 94-128
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ANCIENT SEXUAL PRACTICES - (A.) Serafim, (G.) Kazantzidis, (K.) Demetriou (edd.) Sex and the Ancient City. Sex and Sexual Practices in Greco-Roman Antiquity. (Trends in Classics Supplementary Volume 126.) Pp. xiv + 538, b/w & colour ills. Berlin and Boston: De Gruyter, 2022. Cased, £134.50, €149.95, US$170.99. ISBN: 978-3-11-069577-9.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 140-143
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ecological States: Politics of Science and Nature in Urbanizing China By Jesse Rodenbiker. Cornell University Press, 2023. 264 pages. Hardback, $125.00 USD, ISBN: 9781501768996. Paperback, $24.95, ISBN: 9781501769009. Ebook, free, ISBN: 9781501769016
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Asian Studies / Volume 22 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 185-188
-
- Article
- Export citation
To the Uttermost Parts of the Earth. Legal Imagination and International Power, 1300–1870. By Martti Koskenniemi. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2021. Pp. xviii, 1107. $195.00, hardcover; $99.99, paper.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Economic History / Volume 83 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2023, pp. 1261-1263
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Income tax reductions in production networks
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 28 / Issue 6 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2023, pp. 1394-1421
-
- Article
- Export citation
Corporate Accountability by Treaty: The New North American Rapid Response Labor Mechanism
-
- Journal:
- American Journal of International Law / Volume 118 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2023, pp. 98-119
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Coping strategies for increased wellbeing and mental health among older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic – a Swedish qualitative study
-
- Journal:
- Ageing & Society / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2023, pp. 617-635
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tensions on the Railway: West Indians, Colonial Hierarchies, and the Language of Racial Unity in West Africa
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of African History / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2023, pp. 388-405
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
JEH volume 83 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Economic History / Volume 83 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2023, pp. f1-f7
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation