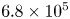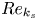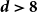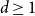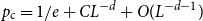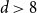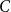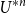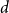Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418807 results in Open Access
The effect of nasal douching by hypertonic 2.3 per cent sea water with algae extracts on the concentration of epidermal growth factor, transforming growth factor-α and interleukin-8 in nasal secretions of patients with nasal polyposis following endoscopic surgical treatment
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, pp. 520-526
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The influence of surface roughness on postcritical flow over circular cylinders revisited
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, A36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
SLA volume 45 issue 5 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Studies in Second Language Acquisition / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, pp. f1-f4
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
SLA volume 45 issue 5 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Studies in Second Language Acquisition / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, pp. b1-b9
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Joyce E. Leader. From Hope to Horror: Diplomacy and the Making of the Rwanda Genocide. Sterling, Virginia: Potomac Books, 2020. xxiii + 384 pp. Map. Bibliography. Index. $50.00. Hardcover. ISBN: 9781640123250.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, pp. 207-209
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Khalid Shamis, dir. The Colonel’s Stray Dogs. 2021. 73 minutes. English. South Africa. Journeyman Pictures. $7.50. https://vimeo.com/ondemand/thecolonelsstraydogs2
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 240-242
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Are dynamic measurements of central venous pressure in Fontan circulation during exercise or volume loading superior to resting measurements?
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 969-980
-
- Article
- Export citation
TRADITIONS OF ROMAN HISTORICAL EPIC - (A.) Augoustakis, (M.) Fucecchi (edd.) Silius Italicus and the Tradition of the Roman Historical Epos. (Mnemosyne Supplements 458.) Pp. xii + 299. Leiden and Boston: Brill, 2022. Cased, €105, US$127. ISBN: 978-90-04-51849-0.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 116-118
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
On sin-based responses to divine hiddenness
-
- Journal:
- Religious Studies / Volume 61 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 650-664
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Emergence of Right-Wing Partisanship in Poland, 1993–2018: Reconciling Demand-Side Explanations of the Success of Illiberalism
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 692-716
- Print publication:
- September 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Tribute to the Behaviour Change Journal, 1984-2023
-
- Journal:
- Behaviour Change / Volume 40 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, p. 253
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Spread-out limit of the critical points for lattice trees and lattice animals in dimensions
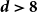 $\boldsymbol{d}\boldsymbol\gt \textbf{8}$
$\boldsymbol{d}\boldsymbol\gt \textbf{8}$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 238-269
-
- Article
- Export citation
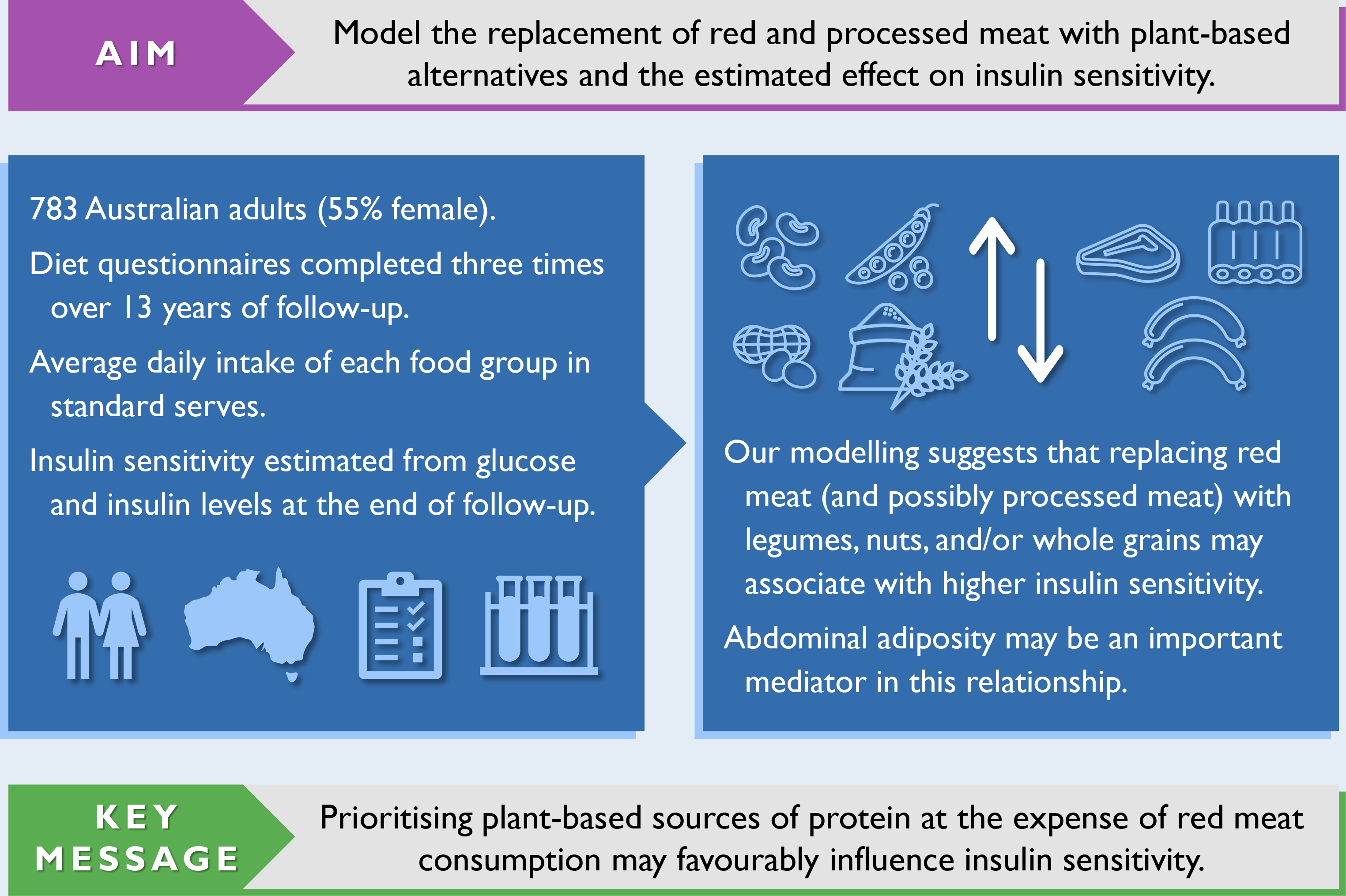
Modelling the replacement of red and processed meat with plant-based alternatives and the estimated effect on insulin sensitivity in a cohort of Australian adults
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 1084-1094
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the Use of Field Recordings on Radio: A history of the beginnings
-
- Journal:
- Organised Sound / Volume 29 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 3-11
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Incest as a rhetorical device: The shock effect of the allegory in Ezekiel 16
-
- Journal:
- Scottish Journal of Theology / Volume 77 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 63-76
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Matthias de Groof, ed. Lumumba in the Arts. Leuven: Leuven University Press, 2020. 400 pp. Illustrations. Map. Bibliography. Index. $79.00. Paper. ISBN: 978-9462701748.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 203-204
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Protecting People from Their Own Religious Communities: Jane Doe in Church and State
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Law and Religion / Volume 38 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 354-375
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pre-Clinical Mobility Limitation (PCML) Outcomes in Rehabilitation Interventions for Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Scoping Review
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 43 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 358-369
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exhibitions, Music and the British Empire. By Sarah Kirby. Martelsham: Boydell Press, 2022. 264 pp. ISBN: 978-1-783-27673-8
-
- Journal:
- Popular Music / Volume 42 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 466-467
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Human Rights: A Key Idea for Business and Society by Karin Buhmann (Routledge, London, 2021). ISBN 9780367520540
-
- Journal:
- Business and Human Rights Journal / Volume 8 / Issue 3 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 480-482
-
- Article
- Export citation