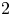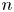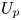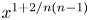Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418807 results in Open Access
A model for the dissipation rate in linear unsteady flow through porous media
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, A42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
“Baked bread to the people”: bread distribution and social and political networks at Pompeii
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Roman Archaeology / Volume 36 / Issue 2 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 519-531
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Slopes in eigenvarieties for definite unitary groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 160 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 52-89
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Do normative data specific to Greek Australian older adults improve validity of neuropsychological assessment results?
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue 10 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 953-963
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
(G.) GREATREX (ed.) with (A.) CAMERON Procopius of Caesarea: The Persian Wars. Translation, with Introduction and Notes. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022. Pp. xxviii + 251. £75. 9781107165700. - (G.) GREATREX Procopius of Caesarea: The Persian Wars. A Historical Commentary. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022. Pp. xxxiii + 851. £140. 9781107053229.
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Hellenic Studies / Volume 144 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 302-304
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prestige, Manipulation, and Coercion: Elite Power Struggles in the Soviet Union and China after Stalin and Mao Joseph Torigian. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 2022, 316 pp. $50.00 (hbk). ISBN 9780300254235
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 257 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 286-287
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mach reflection of three-dimensional curved shock waves on V-shaped blunt leading edges
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, A45
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the representability of actions of Leibniz algebras and Poisson algebras
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 998-1021
-
- Article
- Export citation
The AU Free Movement Protocol: Challenges in Its Implementation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of African Law / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 3-17
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Perceptual alterations in the relationship between sensory reactivity, intolerance of uncertainty, and anxiety in autistic children with and without ADHD
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 37 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 16-28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Moving the boundaries of I-O, or of work itself?
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 16 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 504-507
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of reverberating waves and interface coupling on a divergent Richtmyer–Meshkov instability
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, A44
-
- Article
- Export citation
IOP volunteerism: Acting as individuals, acting as a community
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 16 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 438-442
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Caroline Schaumann. Peak Pursuits: The Emergence of Mountaineering in the Nineteenth Century New Haven: Yale University Press, 2020. Pp. 320.
-
- Journal:
- Austrian History Yearbook / Volume 55 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 472-474
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Career days: Dipping your toe in I-O volunteerism
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 16 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 455-456
-
- Article
- Export citation
JPA volume 97 issue 4 Cover
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 97 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Paediatric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy secondary to Danon disease
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 201-204
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alex Zakaras: The Roots of American Individualism: Political Myth in the Age of Jackson. (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2022. Pp. x, 418.)
-
- Journal:
- The Review of Politics / Volume 86 / Issue 1 / Winter 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 133-135
-
- Article
- Export citation
Intersubstrate Welfare Comparisons: Important, Difficult, and Potentially Tractable
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Land Abundance, Openness, and Industrialization – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- World Trade Review / Volume 22 / Issue 5 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, p. 720
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation