Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1382654 results in Open Access
Identification of Mediating Pathways Between Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Coronary Artery Disease and Heart Failure: A Two-Step Multivariable Mendelian Randomization Study
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dual-function natural biopolymers for aflatoxin M1: adsorption and diagnostic applications in milk
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Tension between Religious Liberty and Religious Establishment in Revolutionary New England
-
- Journal:
- Law and History Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of monsoon waves on the deposition of chitin tubes of polychaetes along the central-eastern Arabian Sea
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 105 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, e140
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tea, ethnography, and social change: a conversation with Chris Hann
-
- Journal:
- New Perspectives on Turkey , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ancient Maya Settlement Buried under Mangroves at Ek Way Nal, Belize
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Antiquity , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
- Export citation
Localised inter-scale energy cascades in free-surface turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1026 / 10 January 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, A51
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reparations as a Driving Force for the Socialization of Industry: The Debate about the Reconstruction of Northern France after World War I from the Perspective of Organized Labour
-
- Journal:
- International Review of Social History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
METHODOLOGIES IN SYSTEMATIC THEOLOGY: A FEW CONTRIBUTIONS, by Louis Roy, Eugene, Oregon, Wipf & Stock, pp. xiii + 111, hbk £29.00
-
- Journal:
- New Blackfriars ,
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Diligent Germans with a Thirst for Knowledge? Emil Schlagintweit, German Orientalism, and Nineteenth-Century Tibetology
-
- Journal:
- Central European History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The pleasure of storytelling: anecdotes in Nikephoros Bryennios’ Material for History
-
- Journal:
- Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
- Export citation
XPS characterization of benzethonium and cetylpyridinium-lauroyl sarcosinate loaded organomontmorillonites and their antibacterial properties against Actinomyces viscosus and Bacteroides fragilis
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-32
-
- Article
- Export citation
Design of a sub-6 GHz cylindrical dielectric resonator MIMO antenna
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
The joint effects of planetary
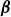 $\boldsymbol{\beta}$, topography and friction on baroclinic instability in a two-layer QG model – CORRIGENDUM
$\boldsymbol{\beta}$, topography and friction on baroclinic instability in a two-layer QG model – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1026 / 10 January 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, E1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Academic environment, directed technical change, and economic growth
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 30 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, e5
-
- Article
- Export citation
The roots of political transformation in Ethiopia: a review essay - ‘Ethiopia’s Developmental State: Political Order and Distributive Crisis’, by Tom Lavers , Cambridge University Press, 2023, 116.71 EUR (Hb), pp. xvi+359, ISBN: 9781009428316 - ‘The Abiy Project: God, Power, and War in the New Ethiopia’, by Tom Gardner , Hurst, 2024, 30£ (Hb), pp. 368, ISBN: 9781911723103 - ‘Greater Tigray and the Mysterious Magnetism of Ethiopia’, by Haggai Erlich , Hurst, 2023, 45£ (Hb), pp. 232, ISBN: 9781805260233
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Modern African Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Clive Brown, Classical and Romantic Performance Practice, Second Edition (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2025), xii + 1061 pp.
-
- Journal:
- Nineteenth-Century Music Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
COHOMOLOGY OF TWISTED POLYNOMIAL SUPERFUNCTORS THROUGH THE TWISTING SPECTRAL SEQUENCE
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 120 / Issue 1 / February 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 78-106
-
- Article
- Export citation
Heidi Hausse. The Malleable Body: Surgeons, Artisans, and Amputees in Early Modern Germany. Manchester: University of Manchester Press, 2023. Pp. 288.
-
- Journal:
- Austrian History Yearbook , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Traditional dishes and culinary improvisations: Elite gastronomy in the Maya area
-
- Journal:
- Ancient Mesoamerica / Volume 36 / Issue 3 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 437-460
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation