Refine search
Actions for selected content:
274907 results in Life Sciences
Development of a robust deep learning model for weed classification across diverse bermudagrass turfgrass regimes in China and the United States
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 73 / Issue 1 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2025, e50
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using population genetics and parentage analysis to detect intergenerational movement distances of flaxleaf fleabane (Conyza bonariensis)
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 73 / Issue 1 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2025, e51
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prevalence of Mollicutes in pregnant women undergoing high-risk prenatal care at a maternal and child reference unit in Bahia, Brazil
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 153 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2025, e73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chemotactic behaviour of Giardia lamblia and Trichomonas vaginalis towards nutrient sources
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 152 / Issue 10 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2025, pp. 1075-1082
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Morphological responses of sorghum seedlings to drought, heat, and combined stresses
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Agriculture / Volume 61 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2025, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Submarine volcanic edifices in the Bransfield Strait (Antarctica): towards a unified toponymy
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Antarctic Science / Volume 37 / Issue 5 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2025, pp. 407-412
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Design and testing of add-on prototypes for transport containers to improve the loading process for end-of-lay hens and catchers
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 34 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2025, e45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Representing Sápmi: Analysing the development of the Saami Council as an Indigenous paradiplomatic organisation
-
- Journal:
- Polar Record / Volume 61 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2025, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A large outbreak of invasive Group B Streptococcus Sequence Type 283 infection linked to physical contact of freshwater fish
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 153 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2025, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Functional response of Chrysoperla externa (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae) to two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae): Implications for biological control
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 115 / Issue 5 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2025, pp. 545-549
-
- Article
- Export citation
Perceptions of preconception health messaging and responsibility: engaging with ‘health helpers’ in the Healthy Life Trajectories Initiative-South Africa trial
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Biosocial Science / Volume 57 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2025, pp. 486-505
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The spread and status of the Gough Moorhen Gallinula comeri on Tristan da Cunha
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 35 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2025, e20
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dietary pattern and lifestyle risk factors for sessile serrated precursors to colorectal cancer
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 134 / Issue 1 / 14 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2025, pp. 35-46
- Print publication:
- 14 July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A survey and analysis of germplasm resources of food crops in Hainan Province
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 23 / Issue 5 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2025, pp. 382-390
-
- Article
- Export citation
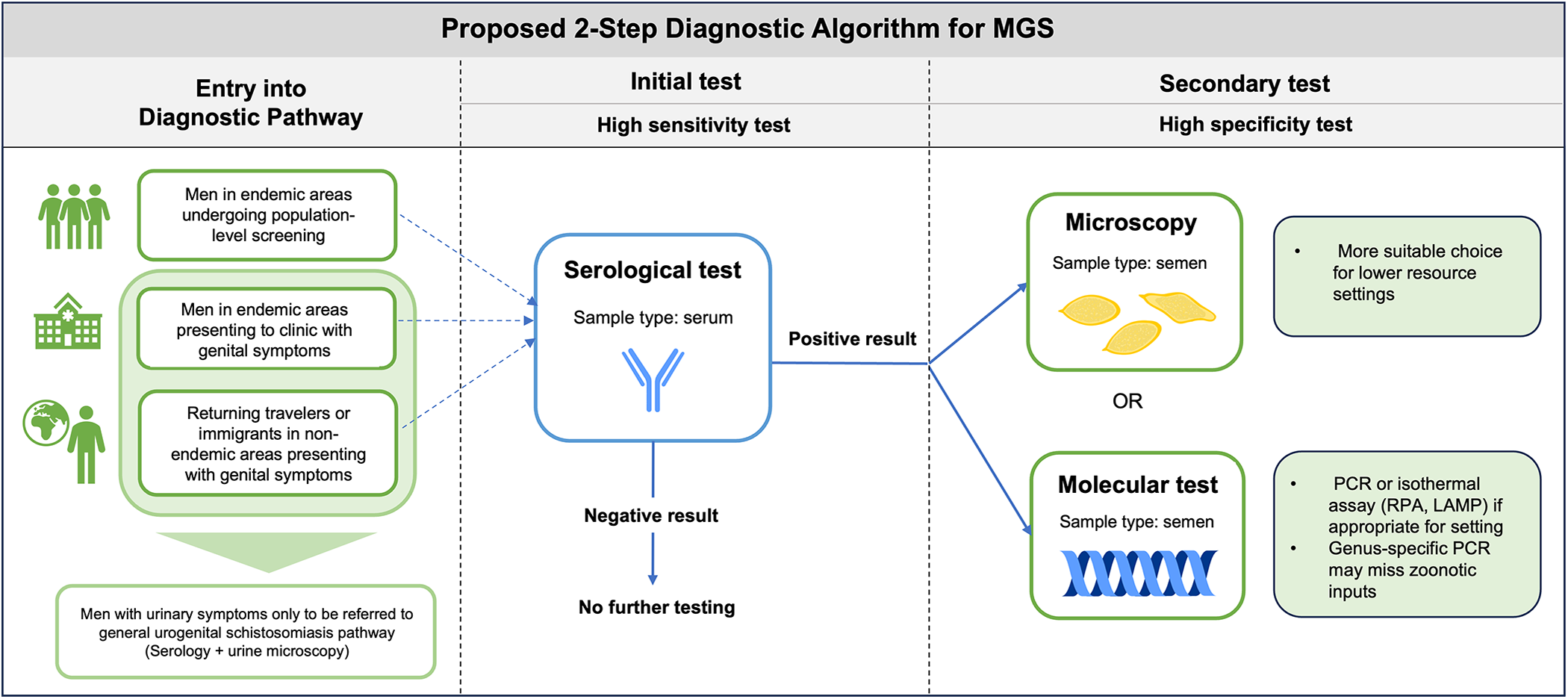
Closing the diagnostic gap in male genital schistosomiasis (MGS): current detection tools and novel strategies
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2025, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Efficacy of pain management for cattle castration: A systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 34 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2025, e43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Control of an outbreak of invasive Group A Streptococcus in a care home in Lincolnshire, England
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 153 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2025, e81
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Factors associated with lower COVID-19 vaccine uptake among populations with a migration background in the Netherlands
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 153 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2025, e87
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multiyear outdoor mesocosm experiment reveals differences in Butomus umbellatus genotype growth and response to herbicides
-
- Journal:
- Invasive Plant Science and Management / Volume 18 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2025, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Navigating the microbial seas: a global analysis of gut microbiota in marine mammals
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 105 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2025, e66
-
- Article
- Export citation