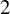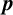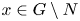Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
599 results in 20Cxx
A local-global principle for unipotent characters
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 December 2024, e125
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A McKay Correspondence in Positive Characteristic
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2024, e116
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON NEIGHBOURHOODS IN THE ENHANCED POWER GRAPH ASSOCIATED WITH A FINITE GROUP
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 112 / Issue 1 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2024, pp. 149-154
- Print publication:
- August 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Counting homomorphisms from surface groups to finite groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2024, pp. 141-153
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Regular Schur labeled skew shape posets and their 0-Hecke modules
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 November 2024, e110
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Quantum wreath products and Schur–Weyl duality I
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 November 2024, e108
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
All Kronecker coefficients are reduced Kronecker coefficients
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Pi / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2024, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fusion Systems and Rank
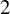 $2$ Simple Groups of Lie Type
$2$ Simple Groups of Lie Type
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, e102
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
THE PRODUCT OF A GENERALIZED QUATERNION GROUP AND A CYCLIC GROUP
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 118 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 November 2024, pp. 31-64
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
ON THE CODEGREES OF STRONGLY MONOLITHIC CHARACTERS OF FINITE GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 111 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2024, pp. 283-289
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
RATIONAL REPRESENTATIONS AND RATIONAL GROUP ALGEBRA OF VZ
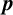 $\boldsymbol {p}$-GROUPS
$\boldsymbol {p}$-GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 118 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 1-30
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Kernels of minimal characters of solvable groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 1167-1170
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An update on Haiman’s conjectures
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, e86
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Improved covering results for conjugacy classes of symmetric groups via hypercontractivity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 October 2024, e85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
VERTEX-PRIMITIVE s-ARC-TRANSITIVE DIGRAPHS OF ALMOST SIMPLE GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 110 / Issue 3 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2024, pp. 566-567
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON MINIMAL DEGREES OF QUOTIENT GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 111 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 October 2024, pp. 177-179
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
FINITE GROUPS WHOSE CHARACTER CODEGREES ARE CONSECUTIVE INTEGERS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 111 / Issue 3 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 October 2024, pp. 513-517
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
FROBENIUS–SCHUR INDICATORS FOR PROJECTIVE CHARACTERS WITH APPLICATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 111 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 290-297
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON NONINNER AUTOMORPHISMS OF SOME FINITE P-GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 111 / Issue 3 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2024, pp. 524-529
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
The structure of finite groups whose elements outside a normal subgroup have prime power orders
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
- Export citation