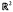Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
415 results in 35Jxx
Three non-trivial solutions for not necessarily coercive p-Laplacian equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 52 / Issue 3 / October 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2009, pp. 679-688
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Positive solutions of a nonlinear Sturm–Liouville boundary-value problem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 52 / Issue 3 / October 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2009, pp. 561-568
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
SIGN-CHANGING SOLUTIONS FOR A CLASS OF NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 80 / Issue 2 / October 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2009, pp. 294-305
- Print publication:
- October 2009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Entire solutions of the differential equation Δ;u = f(u)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 30 / Issue 3 / February 1981
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 366-368
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Higher order elliptic boundary value problems in spaces with homogeneous norms
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 31 / Issue 1 / June 1981
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 92-113
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On the convexity and symmetry of solutions to an elliptic free boundary problem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 42 / Issue 1 / February 1987
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 57-68
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Nonsmooth critical point theory and nonlinear elliptic equations at resonance
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 69 / Issue 2 / October 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 245-271
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Growth of solutions of weakly coupled parabolic systems and Laplace's equation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 41 / Issue 3 / December 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 391-403
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Resolution in hölder spaces of an elliptic problem in an unbounded domain
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 81 / Issue 3 / December 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 387-404
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On a method for constructing Bergman kernels
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 29 / Issue 4 / June 1980
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 454-461
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Monge-Ampère equation and warped products of higher rank
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 83 / Issue 1 / August 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 11-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On the behaviour near the boundary of solutions of a semi-linear partial differential equation of elliptic type
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 31 / Issue 4 / December 1981
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 405-414
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On positive solutions of some semilinear elliptic equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 50 / Issue 3 / June 1991
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 343-355
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Positive solutions of some quasilinear singular second order equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 76 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 125-140
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Some examples related to Kato's conjecture
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 60 / Issue 2 / April 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 274-286
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Second order elliptic boundary value problems in spaces with homogeneous norms
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 29 / Issue 1 / February 1980
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Two estimates concerning asymptotics of the minimizations of a Ginzburg-Landau functional
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 62 / Issue 1 / February 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 128-140
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Partial regularity and everywhere continuity for a model problem from non-linear elasticity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / October 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 158-169
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Multiplicity results for some nonlinear elliptic problems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 76 / Issue 2 / April 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 247-268
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Generalized Emden-Fowler equations of subcritical growth
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / April 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 254-262
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
 to be non-negative, continuous functions,
to be non-negative, continuous functions, 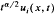 exceeds 1. Related results for Poisson integrals on a half-space are also described, some applications are given, and interesting comparisons emerge.
exceeds 1. Related results for Poisson integrals on a half-space are also described, some applications are given, and interesting comparisons emerge.
 *
*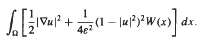 .
.