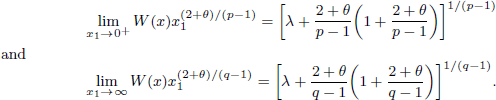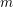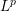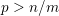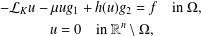Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
416 results in 35Jxx
Infinitely Many Solutions for Schrödinger–Kirchhoff-Type Fourth-Order Elliptic Equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 60 / Issue 4 / November 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2017, pp. 1003-1020
-
- Article
- Export citation
A short remark regarding Pohozaev-type results on general domains assuming finite Morse index
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 147 / Issue 2 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2017, pp. 293-297
- Print publication:
- April 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Infinitely many non-radial solutions for the polyharmonic Hénon equation with a critical exponent
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 147 / Issue 2 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2017, pp. 371-396
- Print publication:
- April 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the Hardy–Sobolev equation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 147 / Issue 2 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2017, pp. 299-336
- Print publication:
- April 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Neumann to Steklov eigenvalues: asymptotic and monotonicity results
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 147 / Issue 2 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2017, pp. 429-447
- Print publication:
- April 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Existence results for semilinear problems in the two-dimensional hyperbolic space involving critical growth
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 147 / Issue 1 / February 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2017, pp. 141-176
- Print publication:
- February 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
MINIMIZING DIRICHLET EIGENVALUES ON CUBOIDS OF UNIT MEASURE
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 63 / Issue 2 / 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2017, pp. 469-482
- Print publication:
- 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Theorems of the Phragmén–Lindelöf Type for Subfunctions in a Cone
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 60 / Issue 3 / August 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 December 2016, pp. 739-751
-
- Article
- Export citation
EXISTENCE OF POSITIVE SOLUTION FOR INDEFINITE KIRCHHOFF EQUATION IN EXTERIOR DOMAINS WITH SUBCRITICAL OR CRITICAL GROWTH
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 103 / Issue 3 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2016, pp. 329-340
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A Static Condensation Reduced Basis Element Approach for the Reynolds Lubrication Equation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / January 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 December 2016, pp. 126-148
- Print publication:
- January 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Optimal Hardy inequalities in cones
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 147 / Issue 1 / February 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2016, pp. 89-124
- Print publication:
- February 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dirichlet problems for fully anisotropic elliptic equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 147 / Issue 1 / February 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2016, pp. 25-60
- Print publication:
- February 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multiple solutions for a critical fractional elliptic system involving concave–convex nonlinearities
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 146 / Issue 6 / December 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2016, pp. 1167-1193
- Print publication:
- December 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multiplicity of Multi-Bump Type Nodal Solutions for A Class of Elliptic Problems with Exponential Critical Growth in ℝ2
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 60 / Issue 2 / May 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2016, pp. 273-297
-
- Article
- Export citation
Asymptotic behaviour and symmetry of positive solutions to nonlinear elliptic equations in a half-space
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 146 / Issue 6 / December 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2016, pp. 1243-1263
- Print publication:
- December 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
THE MODIFIED QUANTUM WIGNER SYSTEM IN WEIGHTED
 $L^{2}$ -SPACE
$L^{2}$ -SPACE
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 95 / Issue 1 / February 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2016, pp. 73-83
- Print publication:
- February 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Weak solutions of complex Hessian equations on compact Hermitian manifolds
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 152 / Issue 11 / November 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2016, pp. 2221-2248
- Print publication:
- November 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
EXISTENCE OF A WEAK SOLUTION FOR A CLASS OF FRACTIONAL LAPLACIAN EQUATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 102 / Issue 3 / June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2016, pp. 392-404
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A Simple Method for Computing Singular or Nearly Singular Integrals on Closed Surfaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2016, pp. 733-753
- Print publication:
- September 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
DIRECT EXPRESSION OF INCOMPATIBILITY IN CURVILINEAR SYSTEMS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 58 / Issue 1 / July 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 July 2016, pp. 33-50
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
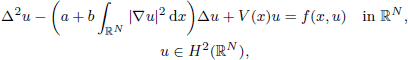
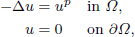
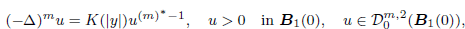
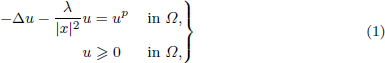
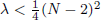 . Using a suitable map we transform problem (1) into another one without the singularity 1/|
. Using a suitable map we transform problem (1) into another one without the singularity 1/|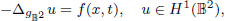
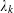
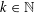
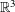
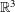
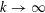
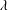
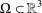
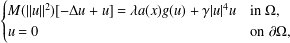
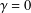
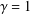
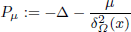
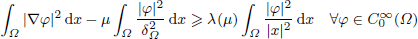
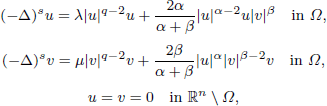
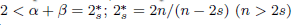 is the fractional critical Sobolev exponent.
is the fractional critical Sobolev exponent.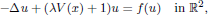
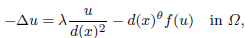
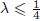 ,
,