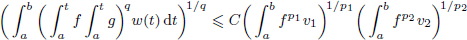Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
325 results in 26xxx
Anisotropic Hardy inequalities
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 148 / Issue 3 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2017, pp. 483-498
- Print publication:
- June 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
A reinterpretation of set differential equations as differential equations in a Banach space
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 148 / Issue 2 / April 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2017, pp. 429-446
- Print publication:
- April 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Which special functions of bounded deformation have bounded variation?
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 148 / Issue 1 / February 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2017, pp. 33-50
- Print publication:
- February 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
A multi-species chemotaxis system: Lyapunov functionals, duality, critical mass
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 29 / Issue 3 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2017, pp. 515-542
-
- Article
- Export citation
ON FUNCTIONS ATTRACTING POSITIVE ENTROPY
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 97 / Issue 1 / February 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2017, pp. 69-79
- Print publication:
- February 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
MAPPING PROPERTIES OF A SCALE INVARIANT CASSINIAN METRIC AND A GROMOV HYPERBOLIC METRIC
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 97 / Issue 1 / February 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2017, pp. 141-152
- Print publication:
- February 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
SOME REVERSE DYNAMIC INEQUALITIES ON TIME SCALES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 96 / Issue 3 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2017, pp. 445-454
- Print publication:
- December 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Fast Evaluation of the Caputo Fractional Derivative and its Applications to Fractional Diffusion Equations: A Second-Order Scheme
- Part of
- Finite fields and commutative rings (number-theoretic aspects)
- Partial differential equations, initial value and time-dependent initial-boundary value problems
- General theory in ordinary differential equations
- Real functions
- Computational aspects
- Miscellaneous topics - Partial differential equations
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 22 / Issue 4 / October 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 July 2017, pp. 1028-1048
- Print publication:
- October 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rank-one convexity implies polyconvexity for isotropic, objective and isochoric elastic energies in the two-dimensional case
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 147 / Issue 3 / June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2017, pp. 571-597
- Print publication:
- June 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
CHARACTERIZATIONS OF THE BOREL
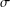 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$ -FIELDS OF THE FUZZY NUMBER SPACE
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$ -FIELDS OF THE FUZZY NUMBER SPACE
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 58 / Issue 3-4 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2017, pp. 265-275
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A Hybrid Spectral Element Method for Fractional Two-Point Boundary Value Problems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Numerical Mathematics: Theory, Methods and Applications / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / May 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2017, pp. 437-464
- Print publication:
- May 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
STABLE, ALMOST STABLE AND ODD POINTS OF DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 96 / Issue 2 / October 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2017, pp. 245-255
- Print publication:
- October 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ON INTEGRAL ESTIMATES OF NONNEGATIVE POSITIVE DEFINITE FUNCTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 96 / Issue 1 / August 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2017, pp. 117-125
- Print publication:
- August 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
EXTENSIONS OF THE HERMITE–HADAMARD INEQUALITY FOR
 $r$ -PREINVEX FUNCTIONS ON AN INVEX SET
$r$ -PREINVEX FUNCTIONS ON AN INVEX SET
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 95 / Issue 3 / June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2017, pp. 412-423
- Print publication:
- June 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
NEW ALGEBRAIC-TRIGONOMETRIC INEQUALITIES OF LAUB–ILANI TYPE
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 96 / Issue 1 / August 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 March 2017, pp. 87-97
- Print publication:
- August 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Curvature-dependent energies: a geometric and analytical approach
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 147 / Issue 3 / June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2017, pp. 449-503
- Print publication:
- June 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
THE CONNECTION BETWEEN PSEUDO ALMOST PERIODIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED ON TIME SCALES AND ON THE REAL LINE
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 95 / Issue 3 / June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2017, pp. 482-494
- Print publication:
- June 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Fast Evaluation of the Caputo Fractional Derivative and its Applications to Fractional Diffusion Equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / March 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2017, pp. 650-678
- Print publication:
- March 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Iterating Bilinear Hardy Inequalities
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 60 / Issue 4 / November 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2017, pp. 955-971
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cosine Radial Basis Function Neural Networks for Solving Fractional Differential Equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2017, pp. 667-679
- Print publication:
- June 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
 -almost everywhere away from the jump set. On the negative side, we construct a function that is BD but not in BV and has distributional strain consisting only of a jump part, and one that has a distributional strain consisting of only a Cantor part.
-almost everywhere away from the jump set. On the negative side, we construct a function that is BD but not in BV and has distributional strain consisting only of a jump part, and one that has a distributional strain consisting of only a Cantor part.
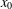
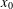
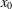
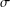
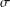
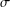
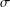
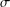
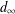
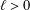
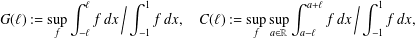
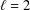
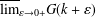
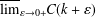
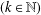
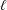


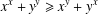
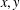
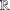
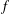
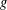
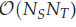 memory and
memory and  work, where
work, where 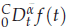 of order
of order 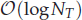 for
for 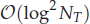 for
for  storage and
storage and 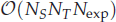 work when numerically solving the time fractional PDEs. Furthermore, we also give the stability and error analysis of the new scheme, and present several numerical examples to demonstrate the performance of our scheme.
work when numerically solving the time fractional PDEs. Furthermore, we also give the stability and error analysis of the new scheme, and present several numerical examples to demonstrate the performance of our scheme.