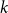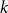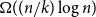Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52651 results in Statistics and Probability
Estimating the share of SARS-CoV-2-immunologically naïve individuals in Germany up to June 2022
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2023, e38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multiple random walks on graphs: mixing few to cover many
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2023, pp. 594-637
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Public health interventions successfully mitigated multiple incursions of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in the Australian Capital Territory
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2023, e30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ECT volume 39 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2023, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Random feedback shift registers and the limit distribution for largest cycle lengths
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2023, pp. 559-593
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exactly solvable urn models under random replacement schemes and their applications
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2023, pp. 835-854
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
ECT volume 39 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2023, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
APR volume 55 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 55 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2023, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Prevalence and persistence of Neisseria meningitidis carriage in Swedish university students
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2023, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Searching for coherence in a fragmented field: Temporal and keywords network analysis in political science
-
- Journal:
- Network Science / Volume 11 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2023, pp. 113-142
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
APR volume 55 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 55 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2023, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Random multi-hooking networks
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 38 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2023, pp. 100-114
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effectiveness of an extra-curricular lecture for STI prevention and sexual education
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2023, e35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Potential analytical interferences when measuring Tmax during temperature programmed pyrolysis of hydrothermally altered volcanoclastic sediment
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2023, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Applied Probability Trust prizes 2022
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2023, p. 366
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identifying spatial and temporal suicide clusters in a Californian county
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2023, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
JPR volume 60 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2023, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
JPR volume 60 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2023, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Sojourn functionals for spatiotemporal Gaussian random fields with long memory
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2023, pp. 148-165
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Epidemiology of herpes simplex virus type 1 and genital herpes in Australia and New Zealand: systematic review, meta-analyses and meta-regressions
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2023, e33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation