Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1422035 results in Open Access
Crystal structure of cariprazine dihydrochloride, C21H34Cl2N4OCl2
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 89-93
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Capital Region in the Unfinished Taiping War
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Chinese History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comorbidities, pharmacologic interventions, and mechanical interventions associated with mortality in isolated diastolic left heart failure: lessons from a national database
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 35 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 102-108
-
- Article
- Export citation
How does ethical climate attract employees’ low-carbon behaviour? The role of environmental passion and green mindfulness
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization / Volume 31 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 103-121
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Rise of the Rich? - Leon Wansleben, The Rise of Central Banks: State Power in Financial Capitalism (Cambridge, Harvard University Press, 2023, 353 p.)
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Sociology / Archives Européennes de Sociologie / Volume 65 / Issue 3 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 490-494
-
- Article
- Export citation
The expression of sICAM-1 influenced by Clonorchis sinensis co-infection in CHB patients
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 98 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, e54
-
- Article
- Export citation
Penumbra Indigo® system to safely remove intracardiac thrombus in a 7-month-old infant with severe immunodeficiency disorder
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 9 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 2039-2041
-
- Article
- Export citation
Determinants of the consumption of ultra-processed foods in the Brazilian population
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 132 / Issue 8 / 28 October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 1104-1109
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
SPANNING TREES IN
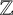 $\mathbb {Z}$-COVERS OF A FINITE GRAPH AND MAHLER MEASURES
$\mathbb {Z}$-COVERS OF A FINITE GRAPH AND MAHLER MEASURES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 118 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 108-144
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tracheostomy in infants in an Australian Tertiary Children’s Hospital: have the indications and outcomes changed?
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 139 / Issue 4 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 311-319
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Magnetic resonance lymphangiography abnormalities as extracardiac biomarkers of pulmonary hypertension and functional phenotype in Fontan-Kreutzer univentricular circulation
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 10 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 2256-2260
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Effects of Post-Earthquake Trauma Levels of Nursing Students on their Academic Motivation and Career Decisions
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, e212
-
- Article
- Export citation
Morphological and molecular characterisation of two new species of Rhipidocotyle (Digenea: Bucephalidae Poche, 1907) from Sphyraena putnamae Jordan & Seale in Mozambique
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 98 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, e56
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Perspective on the health effects of unsaturated fatty acids and commonly consumed plant oils high in unsaturated fat – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 132 / Issue 8 / 28 October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2024, p. 1051
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Middle-Aged Man with Patchy Sensory Deficits in the Face and All Extremities: Introducing an Unusual Phenotype
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 52 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 707-711
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association Between Social Determinants of Health, COVID-19 Stressors, and Mental Health Among New York Residents Early in the Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, e223
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rethinking Animal Consciousness Research to Prioritize Well-Being
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Quarterly of Healthcare Ethics / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 280-284
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PLS volume 43 issue 2 Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Politics and the Life Sciences / Volume 43 / Issue 2 / Fall 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, p. b1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Elizabeth Anderson, Hijacked: How Neoliberalism Turned the Work Ethic against Workers and How Workers Can Take It Back (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023), pp. 384, $29.95 (hardcover). ISBN: 9781009275439.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the History of Economic Thought / Volume 47 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 134-139
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation