Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1382931 results in Open Access
Job Talk: Candidate Gender and Presentation of Prior Experience in Television Ads in the US
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender / Volume 20 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 814-833
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Gender, Religion, and Political Violence: Lessons from Muslim Women’s Experiences in UK Elections
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender / Volume 20 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 834-857
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Responsible Religious Freedom: Factual Scrutiny in Free Exercise Doctrine
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Law and Religion / Volume 39 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 297-321
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A PARAMETERIZED HALTING PROBLEM,
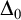 $ \Delta _0$ TRUTH AND THE MRDP THEOREM
$ \Delta _0$ TRUTH AND THE MRDP THEOREM
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic / Volume 90 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 483-508
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
More Than a Journal: Politics & Gender and the Study of Women as National Leaders
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 126-130
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mass-hunting in South-west Asia at the dawn of sedentism: new evidence from Şanlıurfa, south-east Türkiye
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
CONNECTIONS BETWEEN MYTH AND HISTORY - (M.) Christopoulos, (A.) Papachrysostomou, (A.P.) Antonopoulos (edd.) Myth and History: Close Encounters. (MythosEikonPoiesis 14.) Pp. xiv + 423, b/w & colour ills, maps. Berlin and Boston: De Gruyter, 2022. Cased, £124, €139.95, US$157.99. ISBN: 978-3-11-077958-5.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 2 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 375-378
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ventriculocoronary connection with mitral stenosis/aortic stenosis hypoplastic left heart: a case report
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 9 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 2052-2054
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exploring relationships between parental stress, coping, and psychological outcomes for parents of infants with CHD
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 10 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 2189-2200
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Civic Organizations and the Political Participation of Cross-Pressured Americans: The Case of the Labor Movement
-
- Journal:
- American Political Science Review / Volume 119 / Issue 3 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 1173-1189
- Print publication:
- August 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Legendre quadrature for the discretization of 1D radiating panels
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 16 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 49-54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
JAZ volume 117 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 117 / Issue 1 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Racial disparities influence access and outcomes in talking therapies
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 226 / Issue 4 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 203-205
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Flow manipulation of a nematic liquid crystal in a Hele-Shaw cell with an electrically controlled viscous obstruction
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 996 / 10 October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, R1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
NOTICES - (J.) Robson Aristophanes: An Introduction. Pp. xii + 244, ills. London and New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2009 (re-issued in paperback 2024). Paper, £22.99, US$30.95. ISBN: 978-0-7156-3452-3.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 2 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 657-659
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Review of Business and Human Rights: Ethical, Legal, and Managerial Perspectives, Florian Wettstein. (Reviewed by Michelle Westermann-Behaylo)
-
- Journal:
- Business and Human Rights Journal / Volume 9 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 341-342
-
- Article
- Export citation
Acquired multiple coronary artery fistulas: a rare complication of congenital heart surgery in a child diagnosed with right heart valve endocarditis
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 9 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 2046-2048
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rank-one non-singular actions of countable groups and their odometer factors
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 1078-1128
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Beyond brain injury: Examining the neuropsychological and psychosocial sequelae of post-traumatic epilepsy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 8 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 777-784
-
- Article
- Export citation









 of cofinite subgroups in
of cofinite subgroups in 



