Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1382931 results in Open Access
Matthew L. Becker, Fundamental Theology. A Protestant Perspective. Second Edition. London: T&T Clark, Bloomsbury Publishing Pic. 2024. 735 pages.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Anglican Studies / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 278-280
-
- Article
- Export citation
A NOTE ON
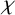 $\chi $-BINDING FUNCTIONS AND LINEAR FORESTS
$\chi $-BINDING FUNCTIONS AND LINEAR FORESTS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 112 / Issue 1 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 23-29
- Print publication:
- August 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Apocalypse in Reformation Nuremberg: Jews and Turks in Andreas Osiander's World By Andrew L. Thomas. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 2022. Pp. xiv + 365. Cloth $85.00 ISBN: 978-0472133208.
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 257-259
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fire and Steel: The End of World War Two in the West By Peter Caddick-Adams. New York: Oxford University Press, 2022. Pp. vii + 652. Hardcover $34.95. ISBN: 978-0190601867.
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 291-293
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pastoral Care and Community in Late Medieval Germany: Albert of Diessen's Mirror of Priests By Deeana Copeland Klepper. Ithaca and London: Cornell University Press, 2022. Pp. xvi + 215. Hardcover $54.95. ISBN: 978-1501766152.
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 254-255
-
- Article
- Export citation
Feminist Foreign Policy in Theory and in Practice: An Introduction. By Stephenie Foster and Susan A. Markham. New York: Routledge, 2024. 154 pp. $48.95 (paperback), $136.00 (hardcover). ISBN: 9781032281667
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 732-734
-
- Article
- Export citation
Free Berlin: Art, Urban Politics, and Everyday Life By Briana J. Smith. Cambridge, Massachusetts and London: The MIT Press, 2022. Pp. 328. Cloth $29.95. ISBN: 978-0262047197.
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 303-305
-
- Article
- Export citation
Who Hosts? The Correlates of Hosting the Internally Displaced
-
- Journal:
- American Political Science Review / Volume 119 / Issue 3 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 1143-1158
- Print publication:
- August 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lutherische Orthodoxie und konfessioneller Pragmatismus. Kurfürst Joachim Friedrich von Brandenburg zwischen Dynastie, Territorien und Reich By Uwe Folwarczny. Berlin: Duncker & Humblot, 2022. Pp. 625. Hardcover €110.00. ISBN 978-3428182633.
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 261-262
-
- Article
- Export citation
Strange Brethren: Refugees, Religious Bonds, and Reformation in Frankfurt, 1554-1608 By Maximilian Miguel Scholz. Charlottesville and London: University of Virginia Press, 2022. Pp. 262. Cloth $45.00. ISBN: 978-0813946757.
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 259-260
-
- Article
- Export citation
At Eden's Door: The Habsburg Jewish Life of Leon Kellner, 1859-1928 By David Rechter. London: The Littman Library of Jewish Civilization in association with Liverpool University Press, 2023. Pp. xii + 199. Cloth $45.00. ISBN: 978-1789621037.
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 269-271
-
- Article
- Export citation
Children and Future Generations Rights before the Courts: The Vexed Question of Definitions
-
- Journal:
- Transnational Environmental Law / Volume 13 / Issue 3 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 522-546
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Weyl chamber length compactification of the
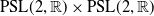 $\textrm{PSL}(2,{\mathbb{R}})\times \textrm{PSL}(2,{\mathbb{R}})$ maximal character variety
$\textrm{PSL}(2,{\mathbb{R}})\times \textrm{PSL}(2,{\mathbb{R}})$ maximal character variety
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 11-33
-
- Article
- Export citation
Colonialism and the Jews in German History: From the Middle Ages to the 20th Century Edited by Stefan Vogt. London and New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2022. Pp. 320. Hardcover $115.00. ISBN: 978-1350155718.
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 273-275
-
- Article
- Export citation
Numerical simulation of different aircraft sub-floor structures during ditching
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1329 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 2530-2544
-
- Article
- Export citation
Deutsch-georgische Zusammenarbeit 1918. Georgiens Unabhängigkeit und das deutsch-georgische Bündnis im Südkaukasus By Giorgi Astamadze. Paderborn: Brill/Schöningh, 2022. Pp. x + 260. Hardcover €89.00. ISBN: 978-3506793669.
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 277-279
-
- Article
- Export citation
What the Ballad Knows: The Ballad Genre, Memory Culture, and German Nationalism By Adrian Daub. New York: Oxford University Press, 2022. Pp. 288. Hardcover $74.00. ISBN: 978-0190885496.
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 266-267
-
- Article
- Export citation
Emergent veno-arterial extra-corporeal membrane oxygenator support for refractory acute myocarditis in paediatric patients
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 10 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 2112-2114
-
- Article
- Export citation
Schinkels Brunnen und das Königsgrab an der Saar. Eine Gedächtnisgeschichte und politische Affäre Preussens By Heinz-Dieter Heimann. Berlin: Duncker & Humblot, 2022. Pp. 187. Hardcover €39.90. ISBN: 978-3428183852.
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. 267-269
-
- Article
- Export citation
8th World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery (WCPCCS) Saturday, August 26, 2023 – Friday, September 1, 2023
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue S1 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2024, pp. S1-S1518
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation