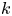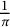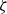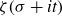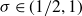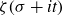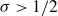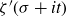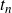Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419237 results in Open Access
Impact of Sharing Dance Older Adults on Physical and Psychosocial Outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 43 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 297-310
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Delegated legislation in the pandemic: further limits of a constitutional bargain revealed
-
- Journal:
- Legal Studies / Volume 43 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 695-733
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prevalence of thyroid gland tissue in midline neck dermoid cysts in children and a proposed new ‘thyroglossal entrainment’ hypothesis for their formation
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 448-450
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prevalence and Distribution of Lewy Pathology in a Homeless Population
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 4 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 496-502
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Long-time dynamics and semi-wave of a delayed nonlocal epidemic model with free boundaries
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 564-610
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterisation of unsteady separation in a turbulent boundary layer: Reynolds stresses and flow dynamics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, A36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Management strategies to improve forage accumulation and nutritive value in crabgrass hayfields
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 161 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 581-588
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Diet and deprivation in pregnancy: a rat model to investigate the effects of the maternal diet on the growth of the dam and its offspring
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 630-641
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
New insight into inheritance pattern of seed coat colour in adzuki bean
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 298-303
-
- Article
- Export citation
INS volume 29 issue 9 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue 9 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. f1-f4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Ramanujan-type series for
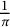 $\frac {1}{\pi }$, revisited
$\frac {1}{\pi }$, revisited
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 350-368
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Overcoming Arbitrage Limits: Option Trading and Momentum Returns
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Volume 59 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 97-120
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Eleni Hasaki. Potters at Work in Ancient Corinth: Industry, Religion, and the Penteskouphia Pinakes (Hesperia Supplement 51. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 2021, 448pp., 247 illustr. including 13 tables, 8 in colour, pbk., ISBN 9780876615539)
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Archaeology / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 531-535
-
- Article
- Export citation
Recent Approaches to the Study of Health, Healing, Illness, and Care in Africa
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 1045-1053
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Spirals of Riemann’s Zeta-Function — Curvature, Denseness and Universality
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 176 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 325-338
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exploring sensory processing abilities in adults with acquired hearing loss
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 496-502
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Naoíse Mac Sweeney. 2023. The West: A New History of an Old Idea (London: W.H. Allen [Penguin Random House], 2013, 437 pp., 14 illustr., hbk ISBN 978-0-7535-5892-8)
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Archaeology / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 542-547
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Sendai Framework Eight Years On: Whither the “Science–Policy Interface”?
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, e501
-
- Article
- Export citation
A problem of Erdős–Graham–Granville–Selfridge on integral points on hyperelliptic curves
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 176 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 309-323
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Behavioral Account of Opportunistic Diversification: Evidence from Non-Real-Estate Firms’ Investment in Real Estate
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 19 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 1071-1103
-
- Article
- Export citation