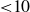Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419357 results in Open Access
MICHAEL H. CRAWFORD, Diocletian’s Edict of Maximum Prices at the Civil Basilica in Aphrodisias with a chapter on the architectural reconstruction by Philip Stinson and contributions by Julia Lenaghan, Benet Salway, Mustafa D. Somersan, Serra Somersan and Yaşar Demiröz (Aphrodisias 13). Wiesbaden: Reichert Verlag, 2023. Pp. xvi + 208; illus, plans. isbn 9783752006858. €89.00.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Successful transcatheter device occlusion of a silent patent ductus arteriosus after treatment for infective endarteritis
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 35 / Issue 6 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1202-1204
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Protestant Hebrew: Performing Religious Authority through Eighteenth-Century Language Production
-
- Journal:
- Religion and American Culture , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Manufactura y distribución de la alfarería San Francisco en los Andes centro sur: Un estudio petrográfico
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Antiquity , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Handling of model uncertainties for underdetermined gas path analysis
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 129 / Issue 1338 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 2263-2282
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Aspherical complex surfaces, the Singer conjecture, and Gromov–Lück inequality
 $\chi \ge |\sigma |$
$\chi \ge |\sigma |$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 179 / Issue 3 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 541-555
- Print publication:
- November 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Beam steering and cross-polarization decoupling enhancement for 4 × 4 microstrip antenna arrays with differential evolution
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 17 / Issue 5 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 774-783
-
- Article
- Export citation
Analysis of 2023 Kahramanmaraş, Türkiye Earthquake Documents in Scopus Database
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 19 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, e192
-
- Article
- Export citation
Correspondence on “Evaluating University and Surrounding Area Factors Causing Variability in COVID-19 Vaccine Rates Among United States Universities”
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 19 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, e190
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A survey and analysis of germplasm resources of food crops in Hainan Province – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 23 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, p. 449
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Thermoviscous localisation of volcanic eruptions is enhanced by variations in fissure width
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Interaction of a vortex ring with a buoyant spherical particle: effects of particle size on vorticity dynamics and particle dynamics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterization of the Yazlıca celadonitic clays (Kütahya, Türkiye) and their potential uses in the ceramic industry
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 60 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 173-190
-
- Article
- Export citation
Experimental investigation of two-dimensional Rayleigh–Taylor instability with controllable initial conditions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A10
-
- Article
- Export citation
New insights into the cavitation erosion by bubble collapse at moderate stand-off distances
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A33
-
- Article
- Export citation
JEROEN W. P. WIJNENDAELE (Ed.), Late Roman Italy: Imperium to Regnum. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2023. Pp. xv + 504, illus. isbn 9781399518024 £155.00 (hbk); 9781399518031, £29.99 (pbk).
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
CHIARA GRAF, Seneca’s Affective Cosmos: Subjectivity, Feeling, and Knowledge in the Natural Questions and Beyond. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press, 2024. Pp. xii + 214. isbn 9780198907008. £76.00.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
RAMSEY-LIKE THEOREMS FOR THE SCHREIER BARRIER
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-29
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cognitive Spontaneity and the Organisation of the Understanding
-
- Journal:
- Kantian Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Book Review: G.A. Cohen: Liberty, Justice and Equality
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation