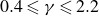Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419572 results in Open Access
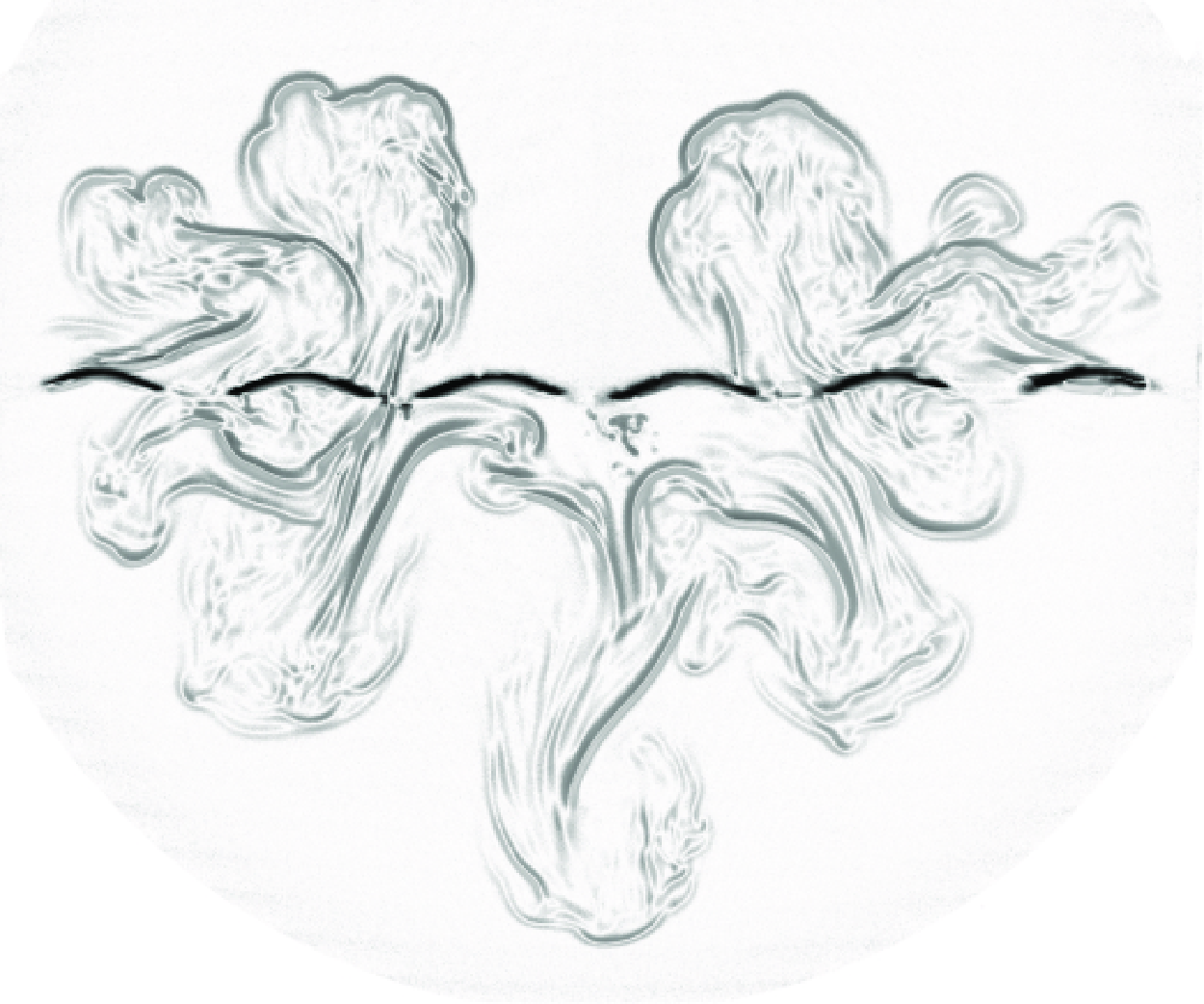
Thermoviscous localisation of volcanic eruptions is enhanced by variations in fissure width
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Interaction of a vortex ring with a buoyant spherical particle: effects of particle size on vorticity dynamics and particle dynamics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterization of the Yazlıca celadonitic clays (Kütahya, Türkiye) and their potential uses in the ceramic industry
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 60 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 173-190
-
- Article
- Export citation
Experimental investigation of two-dimensional Rayleigh–Taylor instability with controllable initial conditions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A10
-
- Article
- Export citation
New insights into the cavitation erosion by bubble collapse at moderate stand-off distances
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A33
-
- Article
- Export citation
JEROEN W. P. WIJNENDAELE (Ed.), Late Roman Italy: Imperium to Regnum. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2023. Pp. xv + 504, illus. isbn 9781399518024 £155.00 (hbk); 9781399518031, £29.99 (pbk).
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
CHIARA GRAF, Seneca’s Affective Cosmos: Subjectivity, Feeling, and Knowledge in the Natural Questions and Beyond. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press, 2024. Pp. xii + 214. isbn 9780198907008. £76.00.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
RAMSEY-LIKE THEOREMS FOR THE SCHREIER BARRIER
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-29
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cognitive Spontaneity and the Organisation of the Understanding
-
- Journal:
- Kantian Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Book Review: G.A. Cohen: Liberty, Justice and Equality
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Extending the mineralogy of U6+ (III.): Pendevilleite-(Y), a new uranyl carbonate mineral from Kamoto-East Open-Cut, Democratic Republic of Congo
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Results of 1470 nanometre diode laser assisted stapedotomy
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 139 / Issue 11 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1050-1054
- Print publication:
- November 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
LUCY GRIG, Popular Culture and the End of Antiquity in Southern Gaul, c. 400–550. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2024. Pp. xviii + 260, illus. isbn 9781108868792. £85.00
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Grassroots quest for upward mobility: Non-elite young Japanese women’s beliefs in global and localized English ideology
-
- Journal:
- English Today , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
- Export citation
Crimes against cultural heritage: World-building at the International Criminal Court
-
- Journal:
- Review of International Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
European Blame Games: Where does the Buck Stop? By Tim Heinkelmann-Wild, Berthold Rittberger, Bernhard Zangl, and Lisa Kriegmair. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2024. 192p.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Journaling During a Disaster: Challenges and Opportunities for Data Collection
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 19 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, e185
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
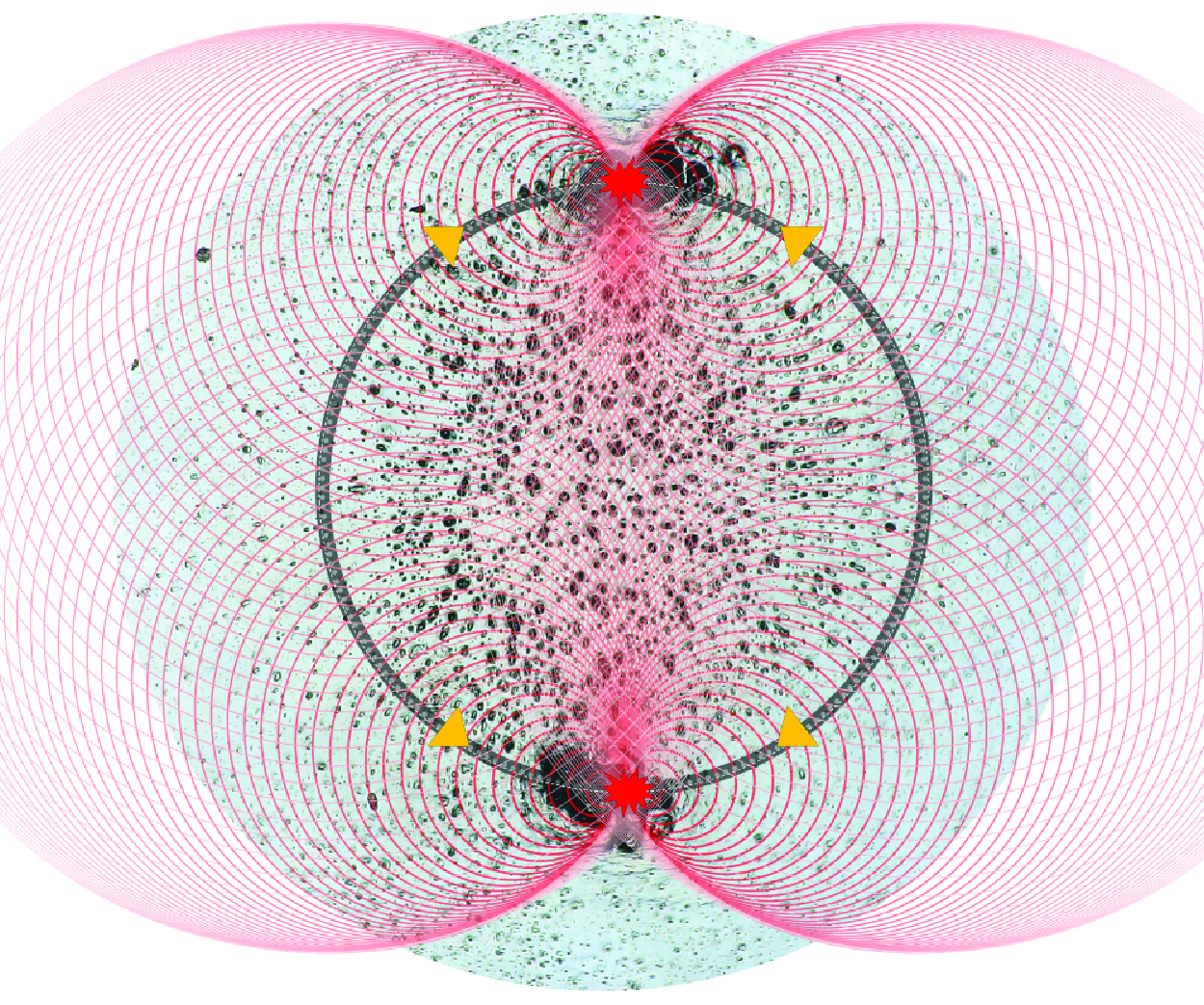
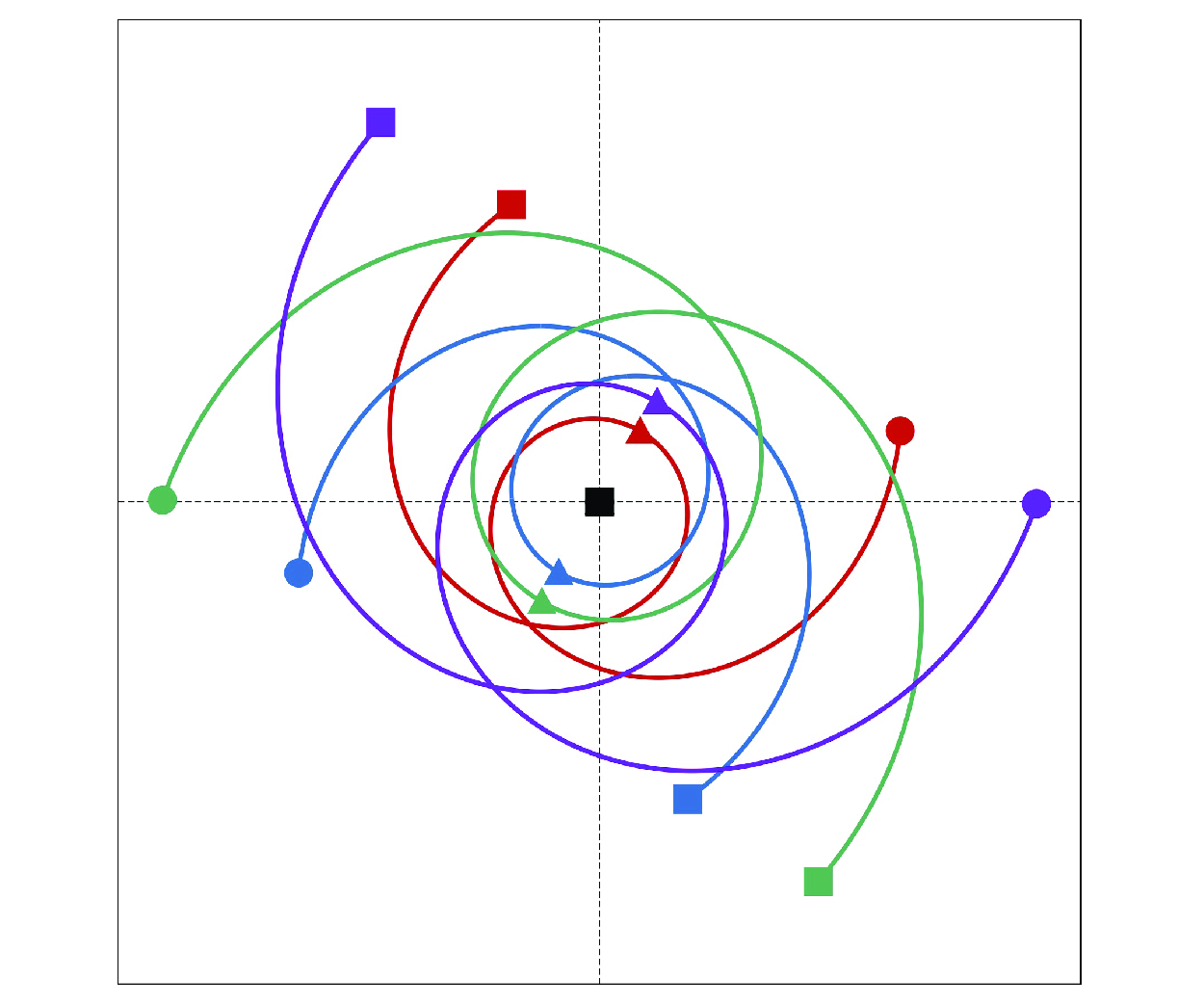
Enstrophy variations in the collapsing process of point vortices
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
One British Archive: ExtraORDINARY Women at Belfast’s Linen Hall Library
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 64 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early outcomes of Myval™ Octacor transcatheter pulmonary valve implantation in dysfunctional right ventricular outflow tract conduits and pulmonary valve bioprostheses: a single-centre UK experience
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 35 / Issue 7 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1408-1414
-
- Article
- Export citation