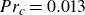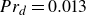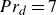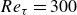Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419572 results in Open Access
Imperial Borderlands: Institutions and Legacies of the Habsburg Military Frontier. By Bogdan G. Popescu. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2024. 317p.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Defending Memory in Global Politics: Mnemonical In/Security and Crisis
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
One British Archive: The Medieval Londoners Database
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 64 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
‘False positive’: understanding pseudocyesis through old and new perspectives
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
- Export citation
Buying People Is Wrong
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 64 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Marine park monitoring informs productivity potential of a southern rock lobster resource in South Australia
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 105 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, e81
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
What’s wrong with motivational interviewing? I. Theoretical and methodological critiques
-
- Journal:
- Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Emerging from the Shadows: Vice Presidential Influence in the Modern Era. By Richard M. Yon. Albany: State University of New York Press, 2024. 402p.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 23 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1200-1201
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Heat transfer in drop-laden low-Prandtl-number channel turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Politics of Language. By David Beaver and Jason Stanley. Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press, 2023. 520p.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 23 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1192-1193
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
In Memoriam: Eric Van Young 1946–2024
-
- Journal:
- The Americas , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Dispersion of Power: A Critical Realist Theory of Democracy. By Samuel Ely Bagg. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2024. 284p.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 23 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1190-1192
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Democracy in Default: Finance and the Rise of Neoliberalism in America. By Brian Judge. New York: Columbia University Press, 2024. 352p.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vessel Wall Imaging for Identifying Symptomatic Atherosclerotic Plaque in Perforating Artery Stroke
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Christopher Ehret. Ancient Africa. A Global History, to 300 CE. Princeton University Press, Princeton (NJ) [etc.] 2023. xii, 210 pp. Ill. Maps. $27.95; £22.00. (Paper, E-book: $19.95; £14.95.)
-
- Journal:
- International Review of Social History / Volume 70 / Issue 1 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 175-178
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multi-asset return risk measures
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 55 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 668-694
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
In Search of Ned: A Zulu Man in Mid-Victorian Britain
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 64 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, e20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Measuring the Quality of Answers in Political Q&As with Large Language Models
-
- Journal:
- Political Analysis , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bogged down ELT, bailed-out CLT?: Translanguaging steps in A context-sensitive response to Bangladesh’s ELT crisis
-
- Journal:
- English Today , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Liberalism as a Way of Life. By Alexandre Lefebvre. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2024. 285p.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 23 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1185-1187
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation