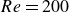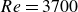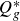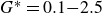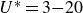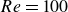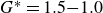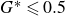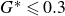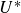Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419563 results in Open Access
Complications of Carotid Artery Stenting: A Real-World Cohort Study in Canada before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Government procurement, climate change perceptions, and corporate green technology innovation in China
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review ,
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vorticity dynamics and drag for flows over a sphere and a prolate spheroid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Traumatic Acute Subdural Hematoma with Actively Bleeding Middle Meningeal Artery
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Techno-natalism: Geopolitical and socioeconomic implications of emerging reproductive technologies in a world of sub-replacement fertility
-
- Journal:
- Politics and the Life Sciences / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / Fall 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 260-279
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A. Martínez-López, J. Mirás-Araujo and N. Rodríguez-Martín (eds.), Economic History of The European Energy Industry: Lighting up Western Europe, 19th to 21st Centuries (Abingdon: Routledge, 2025). Pages xviii + 197 + Figures 24 + tables 31. £145.00 hardback
-
- Journal:
- Continuity and Change , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Patriarchal Political Order: The Making and Unraveling of the Gendered Participation Gap in India. By Soledad Artiz Prillaman. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023. 320p.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
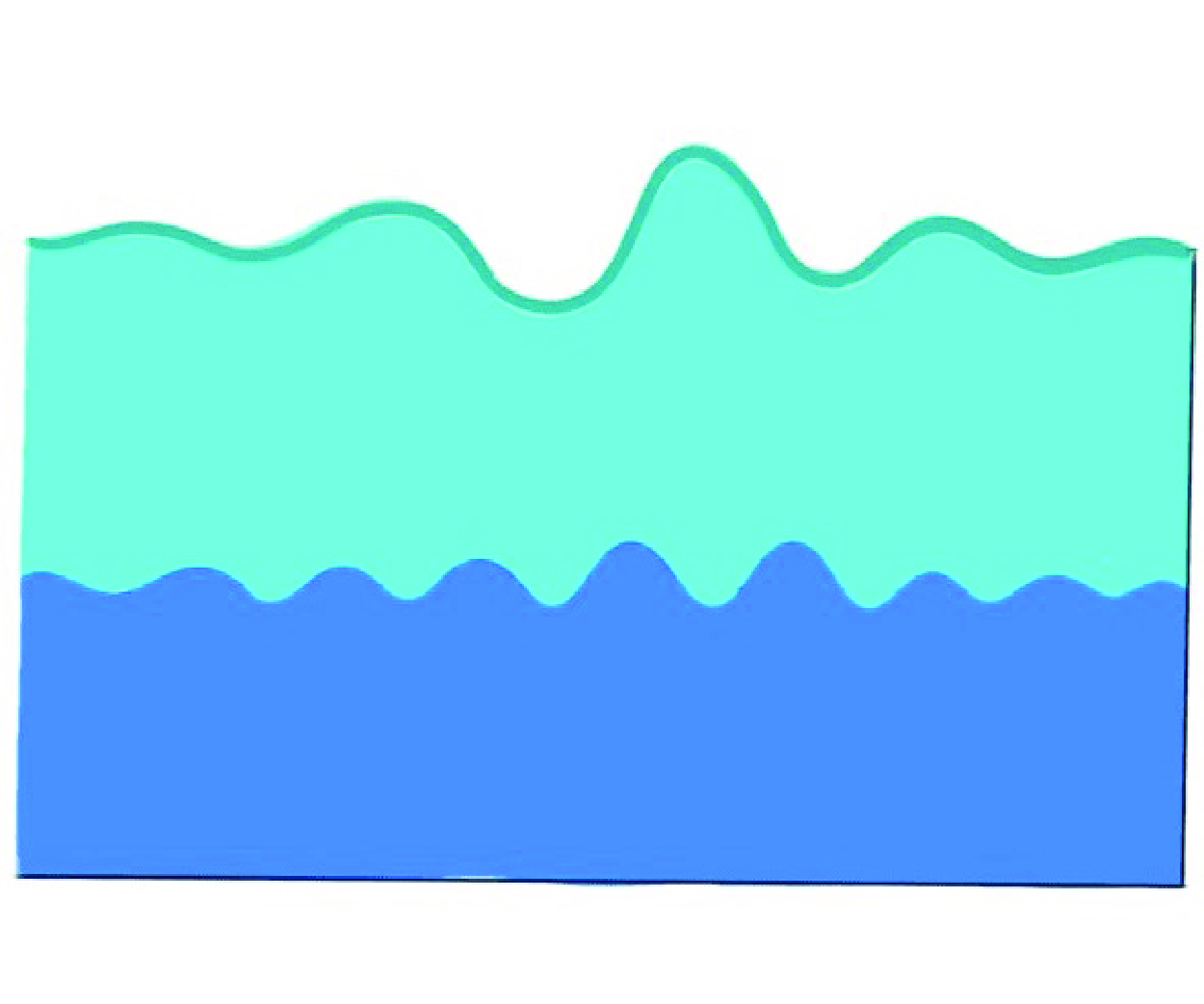
Interactions of flexural-gravity and interfacial waves in a two-layer fluid with a discontinuous background mean flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Recognizing improved Complex Figure memory assessment: The Emory 4-choice Complex Figure recognition task
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Explaining geopolitical inventiveness: Late colonialism, decolonization, and the Cold War (1945–1970)
-
- Journal:
- Social Science History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The End of Peacekeeping: Gender, Race, and the Martial Politics of Intervention. By Marsha Henry. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2024. 200p.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preliminary Report on Symptoms of Anxiety, Depression, and PTSD Following Severe Flooding in Brazil: A Longitudinal Perspective
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 19 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, e189
-
- Article
- Export citation
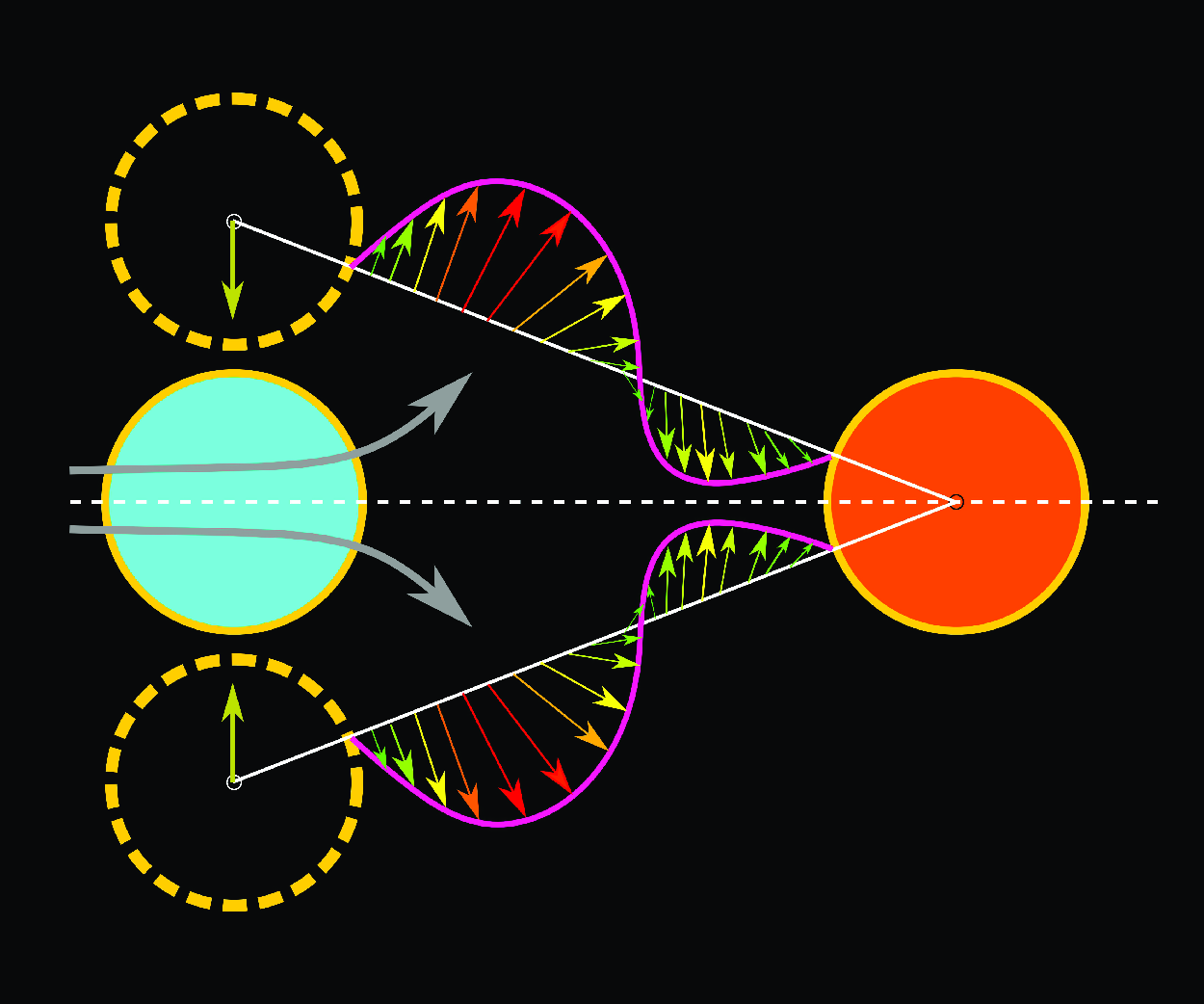
Flow-induced vibration of a cylinder subjected to proximity interference by a downstream-cylinder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Modified design of sub-reflector with dielectric cylindrical keeper to enhance gain in axially displaced ellipse reflector with dual polarization
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 613-619
-
- Article
- Export citation
How large-scale flow structures affect particle transport in wall turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A23
-
- Article
- Export citation
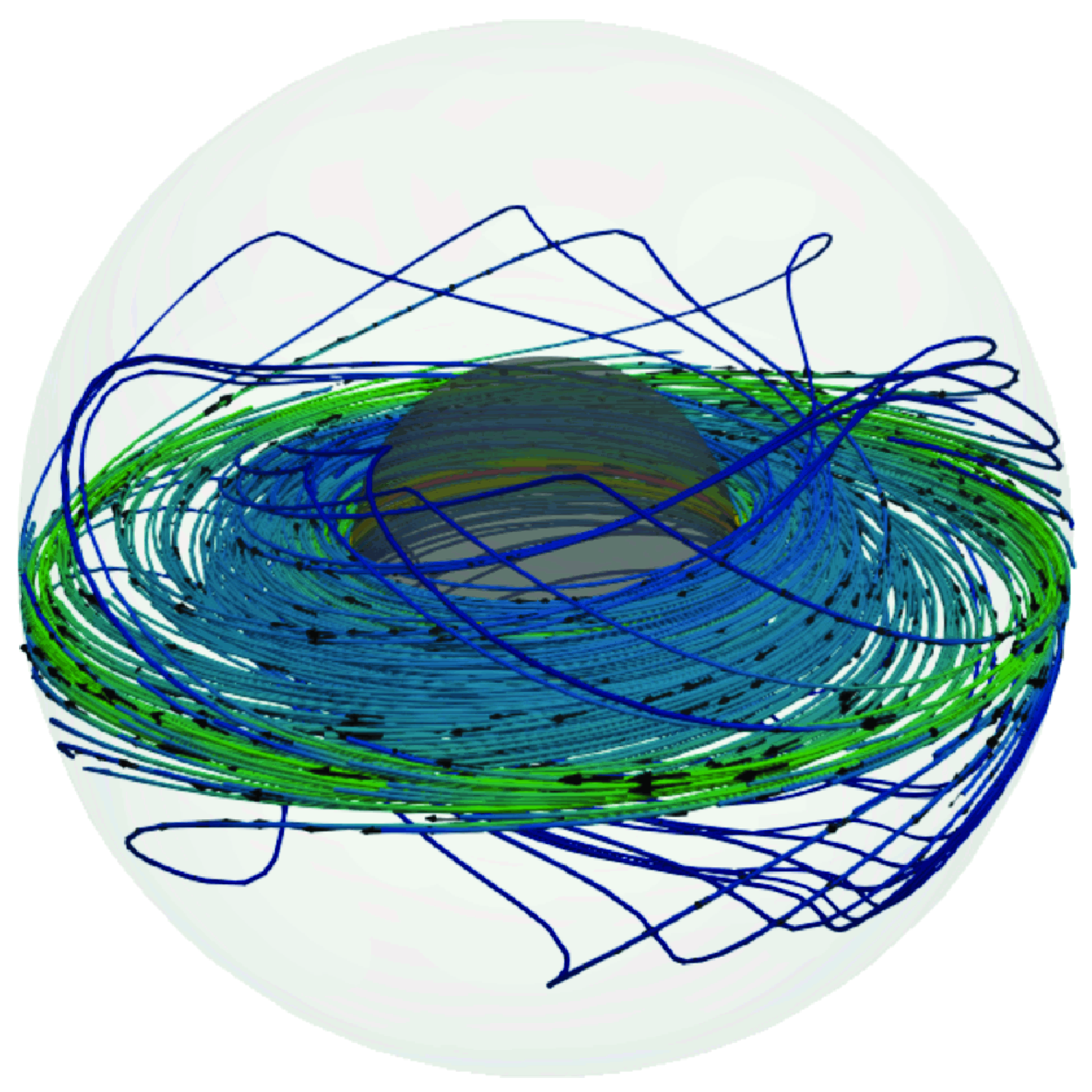
Electromagnetically driven magnetized spherical Couette flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A25
-
- Article
- Export citation
Swimming and mixing of an ellipsoidal squirmer in a viscoplastic fluid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
John James Quinn. Majority State Ownership of Oil and Mining Sectors in Africa: The Resource Curse Undermined. London: Routledge, 2024. xiv + 186 pp. $200.00. Hardback. ISBN: 9781138390331.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
“A Bold Experiment in the Technique of Administration”: Nutrition Science and Development in the Gambia, 1946–50
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 64 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Supreme Prejudice: Examining the Supreme Court’s Racial & Criminal Biases
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Race, Ethnicity and Politics / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 791-813
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation